Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Facultative Anaerobes
Facultative anaerobes are organisms that can survive and grow in both the presence and absence of oxygen. They switch between aerobic respiration when oxygen is available and anaerobic processes when it is not, allowing metabolic flexibility depending on environmental conditions.
Recommended video:
Anaerobic Metabolic Pathways
In the absence of oxygen, facultative anaerobes use anaerobic metabolic pathways such as fermentation or anaerobic respiration to generate energy. These pathways allow the regeneration of NAD+ so glycolysis can continue, producing ATP without the need for oxygen.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Metabolism
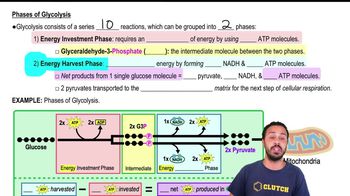
Glycolysis and Energy Harvesting
Glycolysis is the initial step in sugar metabolism, breaking down glucose into pyruvate and producing ATP and NADH. Under anaerobic conditions, glycolysis is coupled with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to regenerate NAD+, enabling continuous ATP production despite the lack of oxygen.
Recommended video: