Young learners of English deserve more
Imagine a class of English language students aged 8 – 9 taught by a dynamic teacher they love. The young learners sit together for two hours, three times a week to learn English as a Foreign Language (EFL). The vibe they bring with them to the class, plus the dynamic teacher and the creativity she develops in her lesson plans, is fantastic.
I have been observing trends in teaching EFL to young learners, and it is clear to me that school directors, syllabus generators, teachers, parents and learners are all satisfied with this image… “Hooray! Young learners sit together for two hours, three times a week to learn English as a Foreign Language. And the teacher is able to manage the class. Bravo!” But is it enough?
What causes the lack of focus?
It all begins with the coursebooks. If you take a coursebook for young learners and thumb through the ‘Scope and Sequence’ pages, you’ll see holistic definitions of language input in each unit. The school authorities then design a course based on the coursebook, and the snowball effect happens, whereby they design a course without specific details on what exactly to focus on.
It is the teacher’s turn now. The creative and dynamic teacher provides an excellent classroom experience through which young learners can learn English together. She also assigns a piece of homework: write an email to a friend and tell her about your last holiday.
When the teacher reviews the emails, she smiles as she finds many uses of the simple past tense—both in affirmative and negative forms. She then drafts an email thanking everyone and praising them generously. She includes a link to a PDF of other exercises to reinforce the grammar (the next day in class, they will review the completed handouts).
This hardworking teacher tries to blend her style with digital literacy and applies creativity along the way. Everything seems perfect in her class, and she regularly receives emails from parents thanking her. Nevertheless, some questions remain: What was the task? What was the learning outcome? Which learning objective should have been tracked?
Let’s reconsider the task – this time with our critic’s hat on – and analyze what has been taking place in this class. It is very nice that young learners sit together to learn English, and the teacher is able to manage the class successfully, but having fun and ease alone is not enough. We should aim for “fun, ease and outcomes”.*
*Assessing Young Learners of English: Global and Local Perspectives, Dr Marianne Nikolov, 2016.
Which important dynamics should be considered?
The assigned piece of homework said: write an email to a friend and tell her about your last holiday. However, what actually occurred was a shift from this task to the students’ best performance in producing simple past-tense sentences. There are other important dynamics that have migrated out of the teacher’s focus. Did the students begin their emails appropriately? Was the tone appropriate? Did they pay attention to organizing their thoughts into sentences and paragraphs? Was the punctuation correct? Did they end their emails in the right way?
If the coursebook had been equipped with clear and concrete learning objectives, the course directors would have employed them while designing study syllabuses, and the teacher would have used them when lesson planning. Consequently, the student’s formative and summative progress would have been evaluated against those detailed learning objectives rather than according to what some did better than the average.
How can learning objectives be applied to tasks?
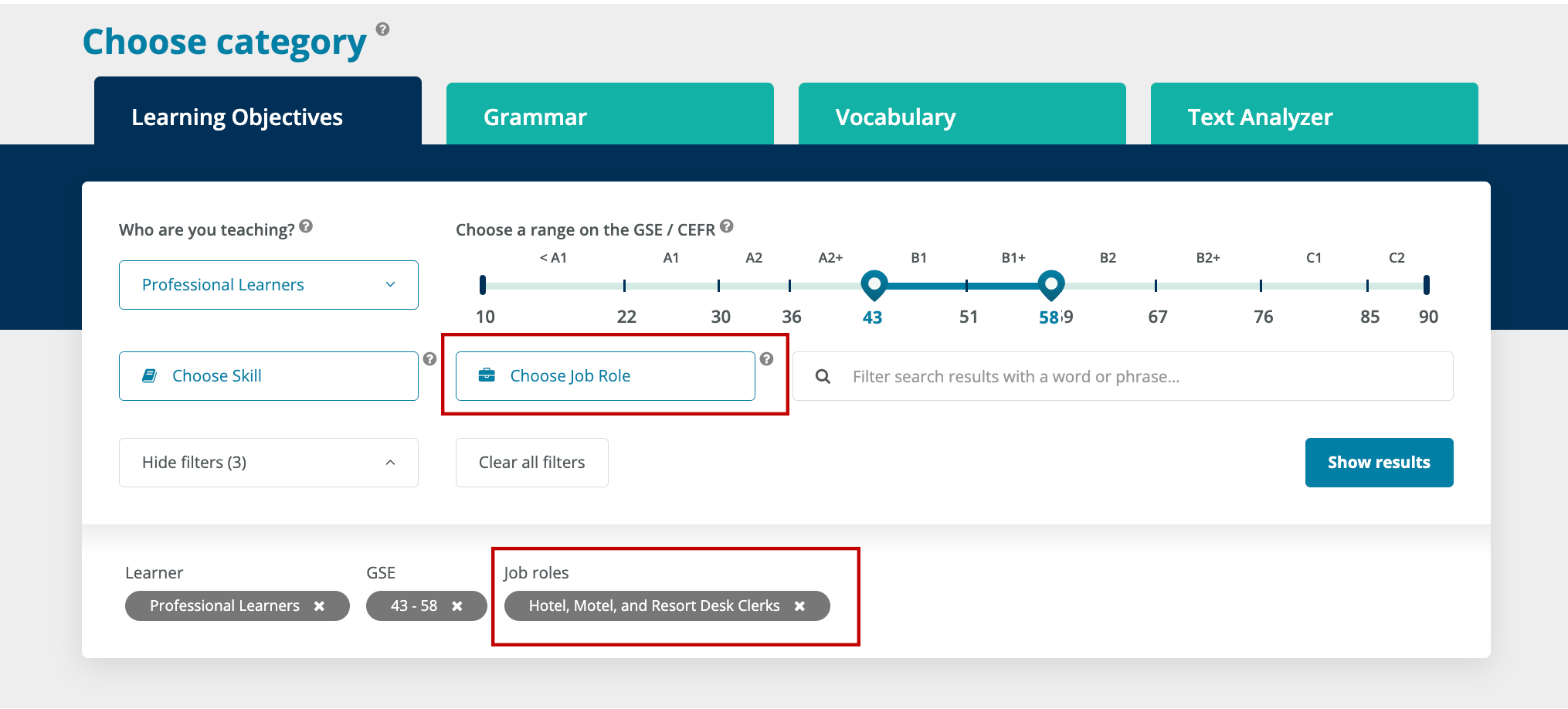
With the Global Scale of English (GSE), publishers, course designers, teachers, and even parents can access a new world of English language teaching and testing. This global English language standard provides specific learning objectives for young learners that can be applied to tasks.
For example, for our task, the GSE suggests the following learning objectives:
- Can write short, simple personal emails/letters about familiar topics, given prompts or a model. (GSE 40/A2+)
- Can use appropriate standard greetings and closings in simple, informal personal messages (e.g., postcards or emails). (GSE: 37/A2+)
By applying language learning chunks – learning objectives, grammar and vocabulary – and identifying the can-do mission each one is supposed to accomplish, teaching and testing become more tangible, practical and measurable. Going back to my original scenario, it is excellent that young learners sit together for two hours, three times a week to learn English as a Foreign Language – provided that we know in detail which learning objectives to focus on, which skills to grow and what learning outcomes to expect.