Back
BackATP quiz #1
You can tap to flip the card.
Control buttons has been changed to "navigation" mode.
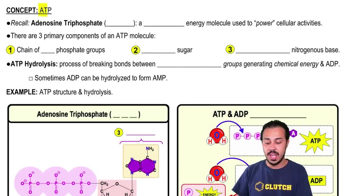
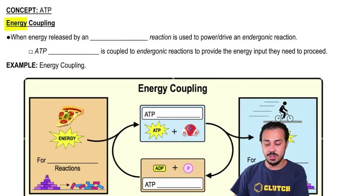
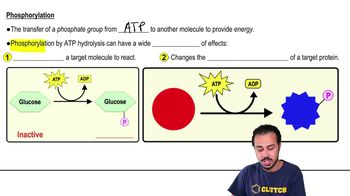
1/10ATP
3. Energy & Cell Processes
3 problems
Topic
Enzymes
3. Energy & Cell Processes
3 problems
Topic
3. Energy & Cell Processes - Part 1 of 4
10 topics 12 problems
Chapter

Bruce
3. Energy & Cell Processes - Part 2 of 4
10 topics 9 problems
Chapter
3. Energy & Cell Processes - Part 3 of 4
8 topics 11 problems
Chapter

Bruce
3. Energy & Cell Processes - Part 4 of 4
7 topics 10 problems
Chapter

Bruce