Membrane Bound Receptors and Secondary Messengers definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackMembrane Bound Receptors and Secondary Messengers definitions
2 students found this helpful You can tap to flip the card.
Control buttons has been changed to "navigation" mode.
1/15
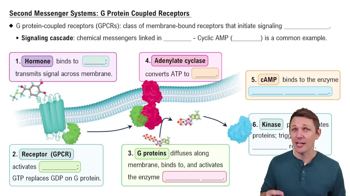
GPCR
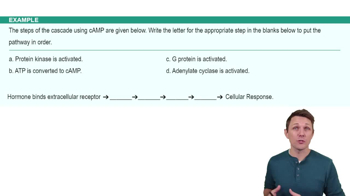
A class of membrane-bound receptors that initiate signaling cascades, crucial for hormone signaling and other sensory functions.Signaling Cascade
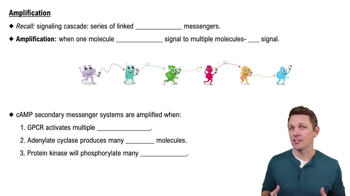
A series of linked chemical messengers that amplify a signal, similar to a waterfall gaining momentum.Cyclic AMP
A secondary messenger produced from ATP by adenylate cyclase, crucial for activating protein kinase A.Adenylate Cyclase
An enzyme that converts ATP to cyclic AMP, playing a key role in the cyclic AMP signaling cascade.Protein Kinase A
An enzyme activated by cyclic AMP that phosphorylates proteins, triggering cellular responses.Amplification
The process where a signal is increased in magnitude as it passes through a signaling cascade.Secondary Messenger
Molecules like cyclic AMP, DAG, and IP3 that relay signals inside the cell, leading to various responses.DAG
A secondary messenger produced by phospholipase C, involved in activating protein kinase C.IP3
A secondary messenger that releases calcium ions from cellular stores, influencing various cellular activities.Vasodilation
The widening of blood vessels, often triggered by cyclic AMP signaling in response to hormones like epinephrine.Vasoconstriction
The narrowing of blood vessels, which can be induced by different signaling pathways in response to hormones.G Protein
A protein activated by GPCRs that transmits signals to enzymes like adenylate cyclase in signaling pathways.Phosphorylation
The addition of a phosphate group to a protein by kinases, altering the protein's function and activity.Hormone
A signaling molecule that binds to specific receptors to induce changes in target cells.Receptor
A protein on the cell surface or inside the cell that binds to specific molecules, initiating a cellular response. Back
Back