Cost of Goods Sold - Perpetual Inventory vs. Periodic Inventory definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCost of Goods Sold - Perpetual Inventory vs. Periodic Inventory definitions
You can tap to flip the card.
Control buttons has been changed to "navigation" mode.
1/15
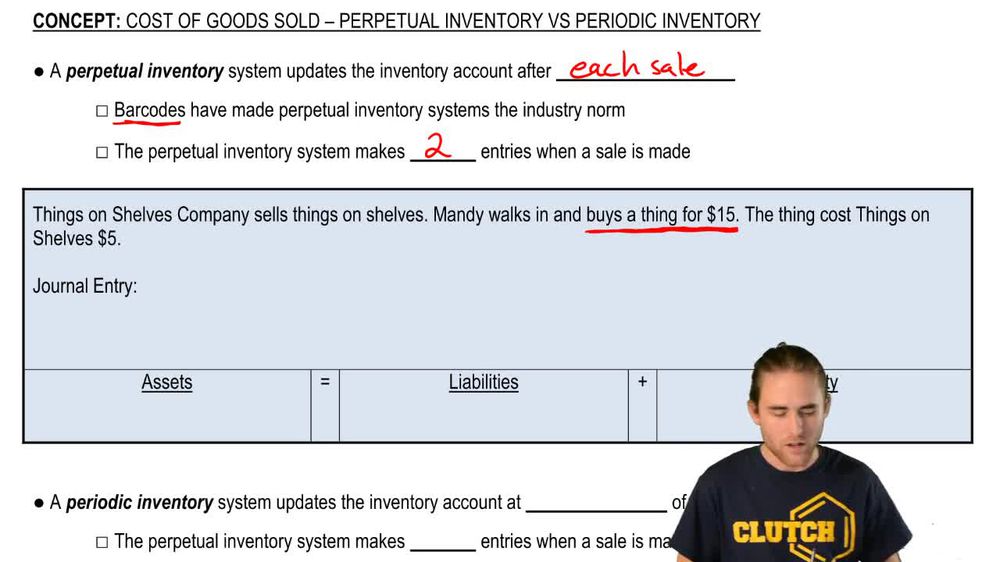
Perpetual Inventory System
Accounting method that updates inventory and cost of goods sold accounts immediately after each sale using real-time data.Periodic Inventory System
Inventory method that updates inventory and calculates cost of goods sold only at the end of the accounting period.Cost of Goods Sold
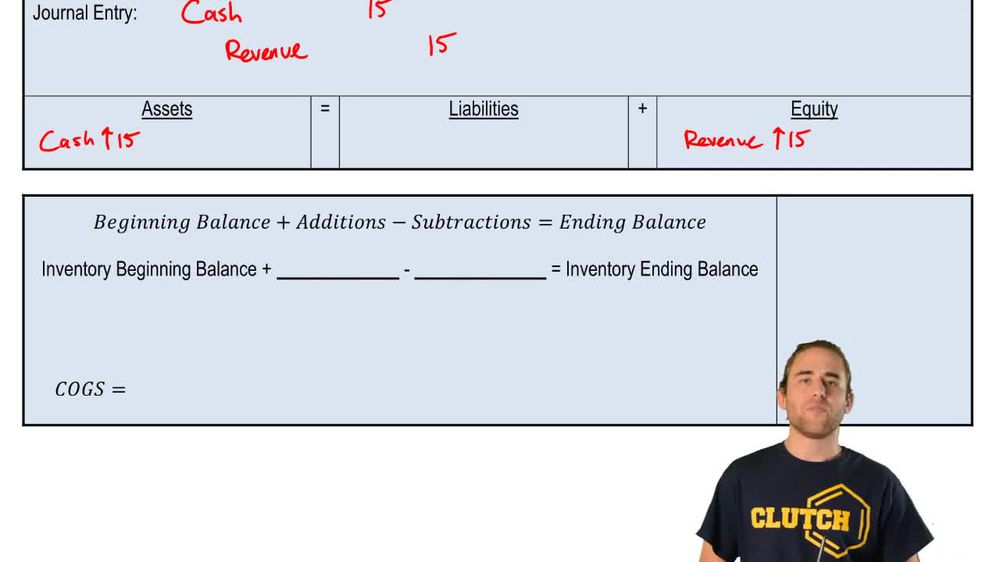
Expense representing the direct cost to acquire or produce items sold during a specific period.Revenue Entry
Journal entry recording the income received from sales, typically involving a debit to cash and a credit to revenue.Inventory Account
Asset account tracking the value of goods held for sale by a business at any given time.T Account
Visual tool used in accounting to represent debits and credits for a particular account, aiding in calculations.Beginning Inventory
Value of inventory a company has on hand at the start of an accounting period.Purchases
Additions to inventory during an accounting period, increasing the inventory account balance.Ending Inventory
Value of inventory remaining unsold at the end of an accounting period, often determined by physical count.Expense Account
Account type used to record costs incurred by a business, such as cost of goods sold, reducing equity.Accounting Equation
Fundamental relationship: Assets = Liabilities + Equity, maintained through all accounting entries.Physical Count
Process of manually counting inventory items to determine the actual quantity on hand at period end.Debit
Accounting entry that increases asset or expense accounts and decreases liability, equity, or revenue accounts.Credit
Accounting entry that increases liability, equity, or revenue accounts and decreases asset or expense accounts.Asset
Resource owned by a business, such as cash or inventory, expected to provide future economic benefit. Back
Back