Photorespiration exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (28)
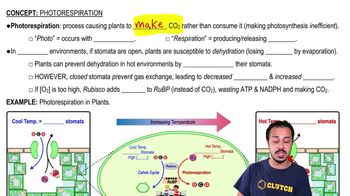
Photorespiration
A process in plants that occurs under hot conditions when stomata close, leading to the production of carbon dioxide and wasting ATP and NADPH.
What happens to stomata in hot environments?
Stomata close to prevent dehydration, which also prevents gas exchange.
RuBisCo
An enzyme that binds oxygen to RuBP during photorespiration instead of carbon dioxide.
Why is photorespiration considered inefficient?
It counteracts the carbon fixation process, wasting ATP and NADPH, and produces carbon dioxide instead of glucose.
Stomata
Openings in plant leaves that control gas exchange and water loss.
What is the main difference between photosynthesis and photorespiration?
Photosynthesis consumes carbon dioxide to produce glucose, while photorespiration produces carbon dioxide and wastes energy.
RuBP
A molecule that binds with carbon dioxide during the Calvin cycle or with oxygen during photorespiration.
What triggers the closing of stomata?
Hot temperatures to prevent water loss through evaporation.
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle is a process in photosynthesis that fixes carbon dioxide to produce G3P, which can be further utilized to synthesize glucose and other carbohydrates.
What happens to oxygen levels when stomata are closed?
Oxygen levels increase inside the plant because it cannot diffuse out.
ATP and NADPH
Energy molecules produced in the light reactions of photosynthesis and wasted during photorespiration.
How does photorespiration affect carbon dioxide levels inside the plant?
Carbon dioxide levels decrease because it cannot enter the plant when stomata are closed.
Gas Exchange
The process of carbon dioxide entering and oxygen leaving the plant through stomata.
What is the role of Rubisco in photorespiration?
Rubisco binds oxygen to RuBP instead of carbon dioxide, leading to photorespiration.
Mesophyll Tissue
The inner tissue of a leaf where photosynthesis and gas exchange occur.
What happens to water molecules when stomata are open?
Water molecules can diffuse out of the plant through evaporation.
Carbon Fixation
The process of converting carbon dioxide into organic compounds during photosynthesis.
Why do plants close their stomata in hot environments?
To prevent dehydration and water loss through evaporation.
Light Reactions
The phase of photosynthesis where light energy is converted into ATP and NADPH.
What is the consequence of RuBisCo binding oxygen instead of carbon dioxide?
It leads to photorespiration, wasting energy and producing carbon dioxide.
Dehydration
The loss of water from a plant, which can be prevented by closing stomata.
What is the relationship between photorespiration and photosynthesis?
Photorespiration competes with photosynthesis by using up resources and producing carbon dioxide.
Stroma
The fluid-filled space inside chloroplasts where the Calvin cycle occurs.
How does photorespiration impact glucose production?
It reduces glucose production by wasting ATP and NADPH and producing carbon dioxide.
Evaporation
The process by which water molecules leave the plant through stomata.
What happens to ATP and NADPH during photorespiration?
They are wasted, making photosynthesis inefficient.
Carbon Dioxide
A gas consumed during photosynthesis and produced during photorespiration.
Why is understanding photorespiration important?
It highlights plant adaptations for managing gas exchange and water loss in varying environments.