Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
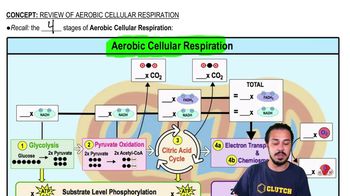
Glycolysis
The first stage of aerobic cellular respiration that breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules, producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytoplasm of the cell.
Pyruvate Oxidation
The second stage of aerobic cellular respiration that converts pyruvates into Acetyl CoA, yielding 2 NADH and releasing 2 CO2.
What are the products of pyruvate oxidation?
2 NADH, 2 Acetyl CoA, and 2 CO2.
Krebs Cycle
The third stage of aerobic cellular respiration that generates 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2 while releasing 4 CO2.
What are two alternative names for the Krebs cycle?
Citric Acid Cycle and Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The final stage of aerobic cellular respiration that produces 26-34 ATP and water, utilizing NADH and FADH2.
What is the role of oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation?
Acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, forming water.
Total ATP yield from one glucose molecule
30-38 ATP.
What is the net ATP gain from glycolysis?
2 ATP.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, creating a proton gradient for ATP synthesis.
What is chemiosmosis?
The process of using a proton gradient to drive ATP synthesis in oxidative phosphorylation.
NADH
An electron carrier that stores energy used to make ATP.
How many NADH are produced in the Krebs cycle?
6 NADH.
FADH2
An electron carrier that stores energy used to make ATP, produced in the Krebs cycle.
How many FADH2 are produced in the Krebs cycle?
2 FADH2.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Direct synthesis of ATP by transferring a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP.
What is the starting molecule for glycolysis?
Glucose.
What is the ending molecule of glycolysis?
2 Pyruvate molecules.
Mitochondrial Matrix
The location within the mitochondria where the Krebs cycle and pyruvate oxidation occur.
How many CO2 molecules are released during the Krebs cycle?
4 CO2.
What is the final product of oxidative phosphorylation?
Water (H2O).
How many ATP are produced in oxidative phosphorylation?
26-34 ATP.
What is the role of the electron transport chain?
To create a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
How many total NADH are produced in aerobic respiration?
10 NADH.
How many total FADH2 are produced in aerobic respiration?
2 FADH2.
What is the efficiency of aerobic respiration?
It can yield 30-38 ATP from one glucose molecule.
What happens to the carbon atoms in glucose during aerobic respiration?
They are converted into carbon dioxide and exhaled.
What is the role of Acetyl CoA in the Krebs cycle?
It enters the Krebs cycle to be further oxidized for energy production.