- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Which of the following properties of carbon allow for the formation of numerous diverse organic compounds?
I. Carbon is tetravalent.
II. It has high catenation ability.
III. Carbon can form multiple bonds and exhibit isomerism.
IV. Carbon has an atomic number of 8.
V. Carbon can be found in all metals.
Is the given property a characteristic of an organic compound with more than thirty carbons?
gas at room temperature
Consider the compound shown below:

Classify whether it is an organic or inorganic compound and identify the type of the formula given (molecular formula, condensed, or extended structural formula).
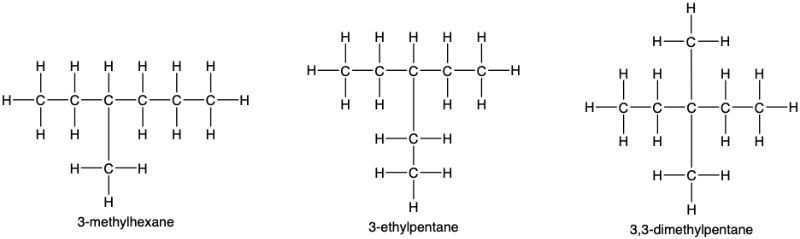
Consider the isomers of heptane shown below:
Give their condensed structures.
Determine if CH3―CH2―O―CH2―CH2―Br is an organic or inorganic compound. Identify the type of formula provided (molecular, expanded, or condensed structural).
Draw a line-angle structure based on the following model. (Blue: C, white: H, red: N)

Which of the following cannot be represented by a skeletal structure?
The structures of organic compounds can be represented using Lewis structures, condensed structural formulas, and skeletal formulas. The compound given below is illustrated using one of the mentioned structural representations. Draw the compound using the other two representations. Note: For the condensed structural formula, represent the parent chain using the condensed formula, and show the bonds for the branches, if applicable.
Consider the molecular model shown below. Draw its skeletal formula and name the functional groups present in the compound.

(Gray = C; white = H; Red = O; Yellow = S)
Name the functional groups highlighted in the molecule shown below.

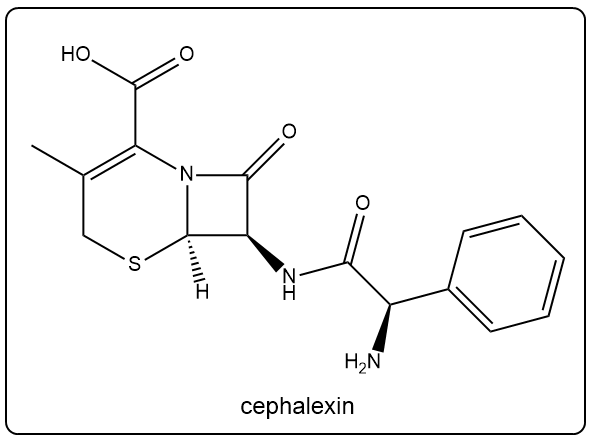
Which of the following functional groups are present in cephalexin's structure? Select all that apply.
I. Amide
II. Carboxylic acid
III. Alcohol
IV. Ester
V. Amine
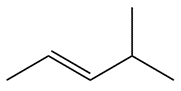
Identify the name and draw the skeletal structure of a straight-chain alkane with the molecular formula C7H16.