- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Determine the kind of inhibition (non-competitive, competitive, or irreversible) present in the following:
A certain pesticide works by attaching itself to an allosteric site on an insect’s digestive enzymes and slowing down their activity without permanently inactivating them.
True or False: A competitive inhibitor can be identified from an uncompetitive inhibitor by increasing the substrate concentration and monitoring the reaction's rate change.
Which type of enzyme inhibitor is often considered poison? Explain your answer.
How does the rate of a biochemical reaction catalyzed by an enzyme change when the concentration of a non-competitive inhibitor is increased, keeping the substrate concentration constant?
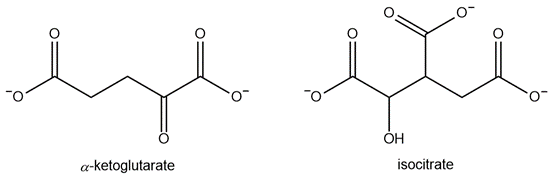
During a biochemical experiment, it was found that α-ketoglutarate acts as an inhibitor of isocitrate dehydrogenase.
Would α-ketoglutarate act as a competitive or noncompetitive inhibitor?
In the treatment of hypertension, a patient is prescribed captopril, a medication known to affect the renin-angiotensin system. Is captopril considered a reversible or irreversible inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)?
Methanol (CH3OH) is a toxic substance that can lead to blindness or death if ingested. It is metabolized in the liver by the same enzyme that metabolizes ethanol. The toxic metabolites of methanol are formaldehyde (HCHO) and formic acid (HCOOH). The administration of an intravenous ethanol solution is used as a treatment for methanol poisoning. How could this method help in preventing the toxic effects of methanol ingestion?