- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A 2 kg object is pushed with an initial speed of 20 cm/s. The object then collides with a horizontal spring having a spring constant of 50 N/m. The object is in contact with the spring for 0.2 seconds before bouncing back. Determine the maximum compression experienced by the spring during the collision.
A person standing on the bridge notices that the bridge starts to vibrate with a frequency of 3.5 Hz when a large truck passes by. If the mass of the bridge is 5000 kg, what is the effective spring constant of the bridge?
A thin metal plate having a mass of 0.25 g is experiencing oscillations. Determine the maximum speed attained by the plate if the frequency of oscillations is 1.5 MHz. The metal plate shows a maximum acceleration of 1.40 × 108 m/s2.
A mass of 25 g attached to a spring undergoes SHM with a frequency of 2.0 Hz and an amplitude of 10.0 cm. If the amplitude decreases to 6.0 cm after 5.0 s due to damping, what is the damping constant of the system?
A young astrophysicist is studying the atmosphere of a newly discovered gas giant planet and is interested in creating a model of acetylene gas. Acetylene consists of two carbon (C) atoms and two hydrogen (H) atoms, as shown below. The C–C and H–C bonds can be considered to be ideal springs with unknown spring constants kC-Cand kH-C, respectively. The symmetric stretch frequency of the carbon-carbon bond in acetylene is measured to be 9.94 x 1013Hz. If the atomic masses of carbon and hydrogen are known to be mC = 12.0 amu and mH = 1.0 amu, respectively, calculate the effective spring constant of the carbon-carbon bond in acetylene.

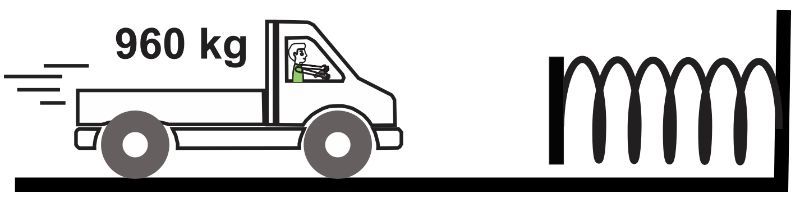
How long does a 960-kg truck remain in contact with a heavy-duty buffer after crashing into it at 26 m/s and compressing it by 6.0 m before it rebounds?
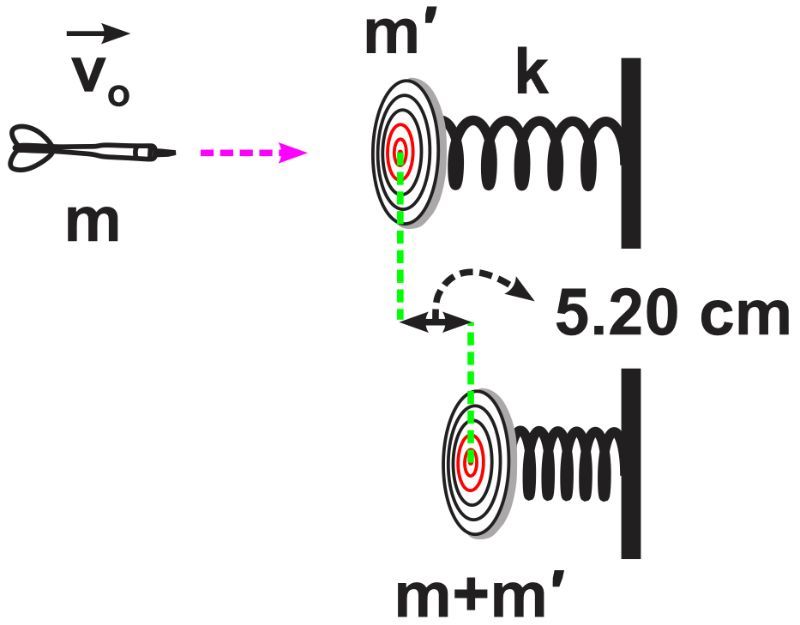
A 5.42 kg dartboard is attached to the free end of a spring that is oriented horizontally. The other end of the spring is fixed to a wall. A student throws a dart of mass 0.0423 kg at the dartboard and it gets stuck in the dartboard. As a result, the spring gets compressed by a maximum distance of 5.20 cm. Given that the spring constant of the spring is k = 122 N/m, find the speed of the dart vo which strikes the dartboard. [Assume that there is no friction involved.]