- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

During a concert, three violin artists are playing the same tune on stage. The placement of the violin artists is depicted in the figure. You are sitting in the audience 8.0 m away in front of the middle artist. Determine the minimum distance through which the middle violin artist must change his position backward so that you can hear maximum sound intensity. Consider the amplitude of the sound is 'A' and the frequency is 425 Hz from each violin. The velocity of sound is 340 m/s.

In an annual gathering of a college, three students are doing a piano show. They are sitting as portrayed in the figure. The college principal is sitting 3.0 m away in front of the middle student playing the piano. The amplitude of the sound played is 'B' at a frequency of 170 Hz by each student. Determine the ratio of the maximum intensity of sound to the sound intensity of a single piano if the sound waves emitted are in phase. Consider the speed of sound is 340 m/s and all the sound measurements are done at the position of Principal.

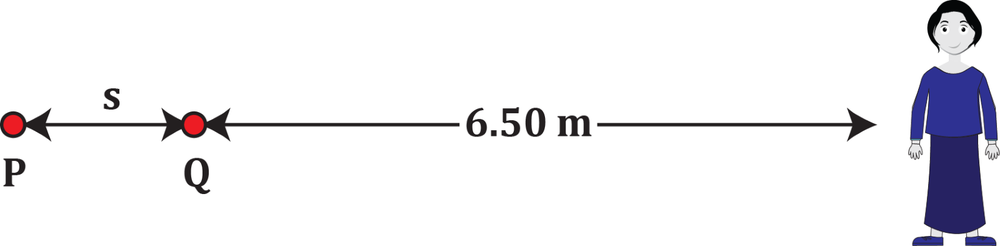
Two identical tuning forks P and Q, placed at the same position, are playing sounds of frequency 650 Hz. A person is 6.50 m away to the right from this initial position. The tuning fork P is gradually moved away to the left while Q is kept still, as shown in the figure. For a certain position of the tuning fork P, the person first hears a destructive interference. Determine the distance between P and Q for which the next destructive interference will be heard. Assume that the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s.
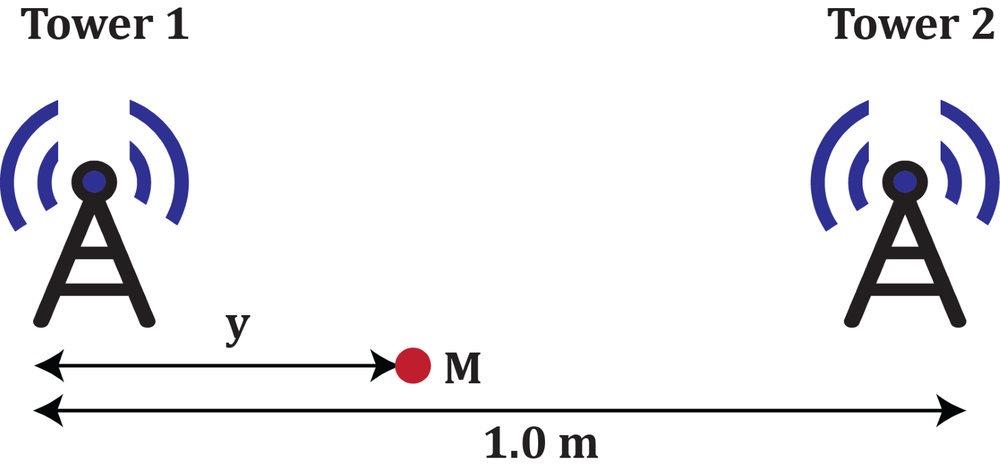
Two synchronized radio towers, Tower 1 and Tower 2, are transmitting signals at the same frequency of 400 Hz. Tower 2 is located exactly 1.0 m north of Tower 1. An observer is located somewhere along the line joining these two towers. If 'y' represents the distance from the observer to Tower 1, then find all possible values for y which would result in destructive interference at the observer's location. Consider the speed of sound in air to be 340 m/s.
When studying water wave interference, one can observe that destructive interference takes place if the waves are out of phase by 1/2 wavelength or 180°. Explain why a 180° phase difference corresponds to 1/2 wavelength in the context of water waves.
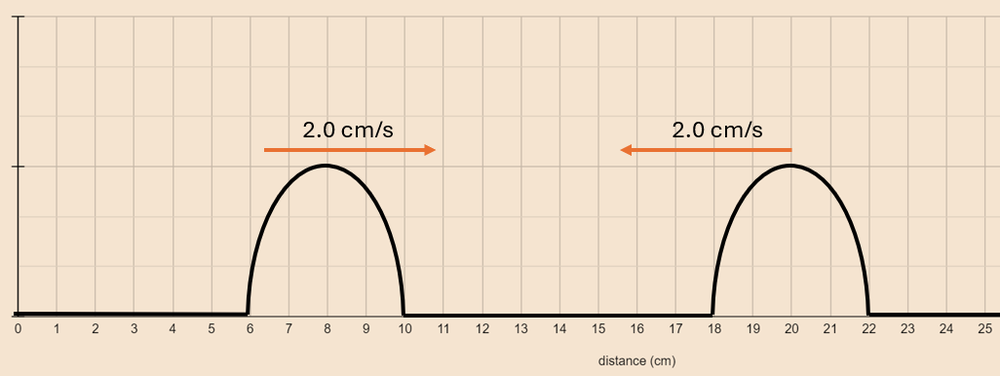
A taut rope, as shown below, has two pulses moving towards each other at a speed of 2.0 cm/s. Sketch the shape of the rope at the end of 3.0 seconds.