- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A competition among kids involves throwing a wooden block of mass 5.0 kg towards a spring with a force constant of 70 N/cm on a flat surface of negligible friction. The winner should produce the greatest compression in the spring. If one kid throws the block at 2.0 m/s, what is the greatest compression observed on the spring?
A technician wishes to perform a repair by riveting an elastic material onto a gap in an object. She cuts 18.0 cm of the material and applies a force of 10.0 N on it. She observes the material increase in length by 4.0 cm. The material is applied on the patch with an elongation of 2.80 cm. Determine the maximum force it applies to the object.
A 30.0 g ball bearing is launched from a stretched elastic cord. The force acting on the ball bearing is plotted in the graph below. The elastic cord was stretched by 20 cm before it was released. Determine the speed of the ball bearing.

Imagine a scenario where a person stands on a spring which is attached to the ground, note that initially the spring is at its natural length and unstressed position. The force exerted by the spring on the person, as the spring is compressed from its natural position when the person stands on the spring will experience a maximum compression of 0.10 meters, and can be described by the function F(y) = (200 N/m)y - (150 N/m2)y2 along the y-axis. Calculate the work done on the person by the spring during the compression of the spring.
In a logistics center, an automated sorting system utilizes a spring mechanism with a spring constant k to lift packages for sorting. To start the elevation of a package with mass m, an applied force is exerted on the spring (with negligible mass). Determine the work required by this applied force on the spring to lift the package just before it starts to leave the support.
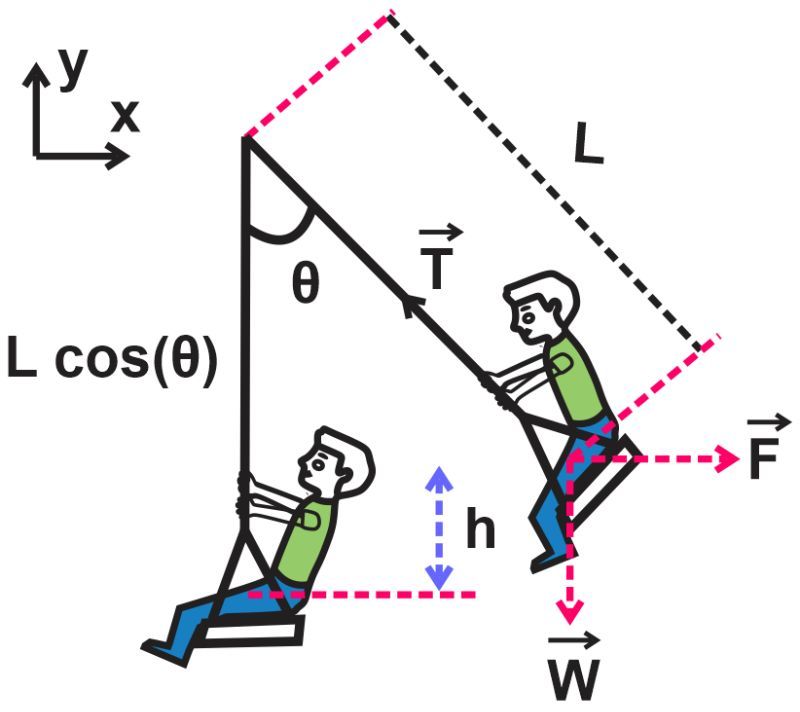
Consider a child sitting in a park swing with a total mass of 30 kg, suspended by chains of length 2.5 meters. To start the swing, a horizontal force F is gently applied to the swing, moving it so slowly that the acceleration of the child is negligible. Compute the work done by this force to move the swing from its stationary position (θ=0°) to an angle θ=15°with the vertical.
An engineer is investigating the properties of a "2 mi/h (3 km/h) spring". He finds that it can compress elastically without permanent deformation if a heavy object of mass 1500 kg hits it with speeds below 3 km/h. In that case, the maximum compression before the spring begins to permanently deform (up to which point the behavior of the spring is elastic) is 2.3 cm. Calculate the effective spring constant of the spring.
An elastic string was stretched from x = 4.0 cm to x = 9.4 cm, where x = 0.0 indicates the string's unstretched length. Drawing a force versus x graph for the string find the work needed to stretch the string. Assume the string has a spring constant K = 44 N/m.