Back
BackBallistic Pendulum quiz #1
You can tap to flip the card.
Control buttons has been changed to "navigation" mode.
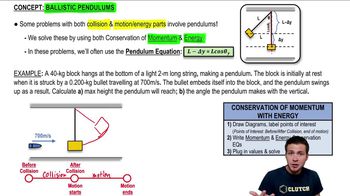
1/10Ballistic Pendulum
11. Momentum & Impulse
2 problems
Topic

Patrick
Collisions with Springs
11. Momentum & Impulse
3 problems
Topic

Patrick
11. Momentum & Impulse - Part 1 of 3
5 topics 11 problems
Chapter

Patrick
11. Momentum & Impulse - Part 2 of 3
5 topics 11 problems
Chapter

Patrick
11. Momentum & Impulse - Part 3 of 3
5 topics 11 problems
Chapter

Patrick