Best Practices for Implementing a Community Oriented Career & Technical Program
by Iman Moore
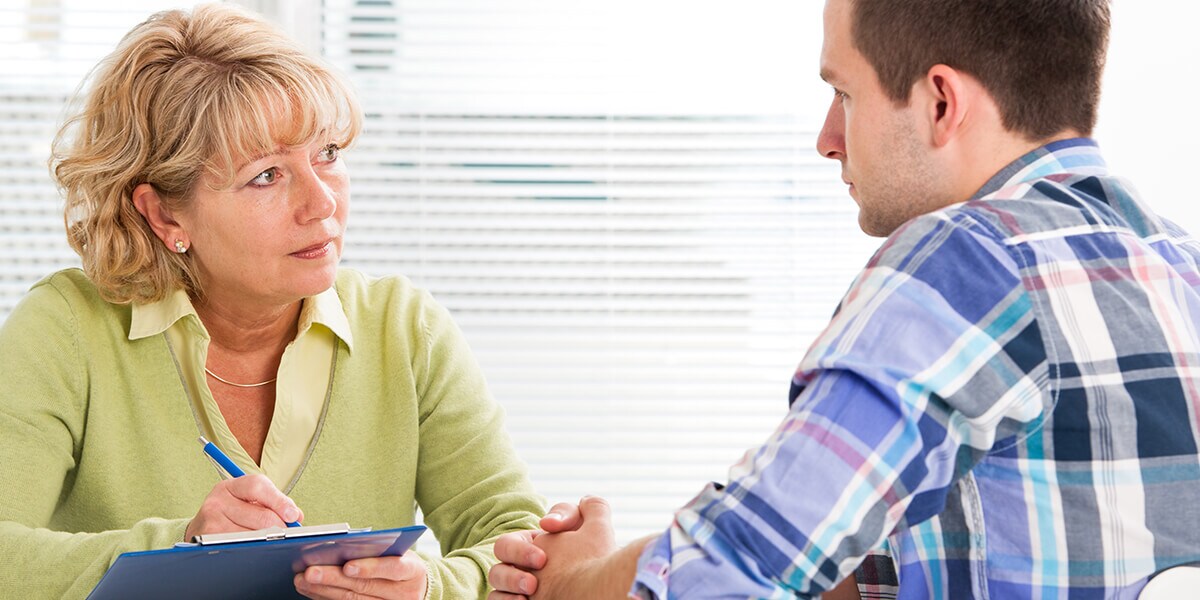

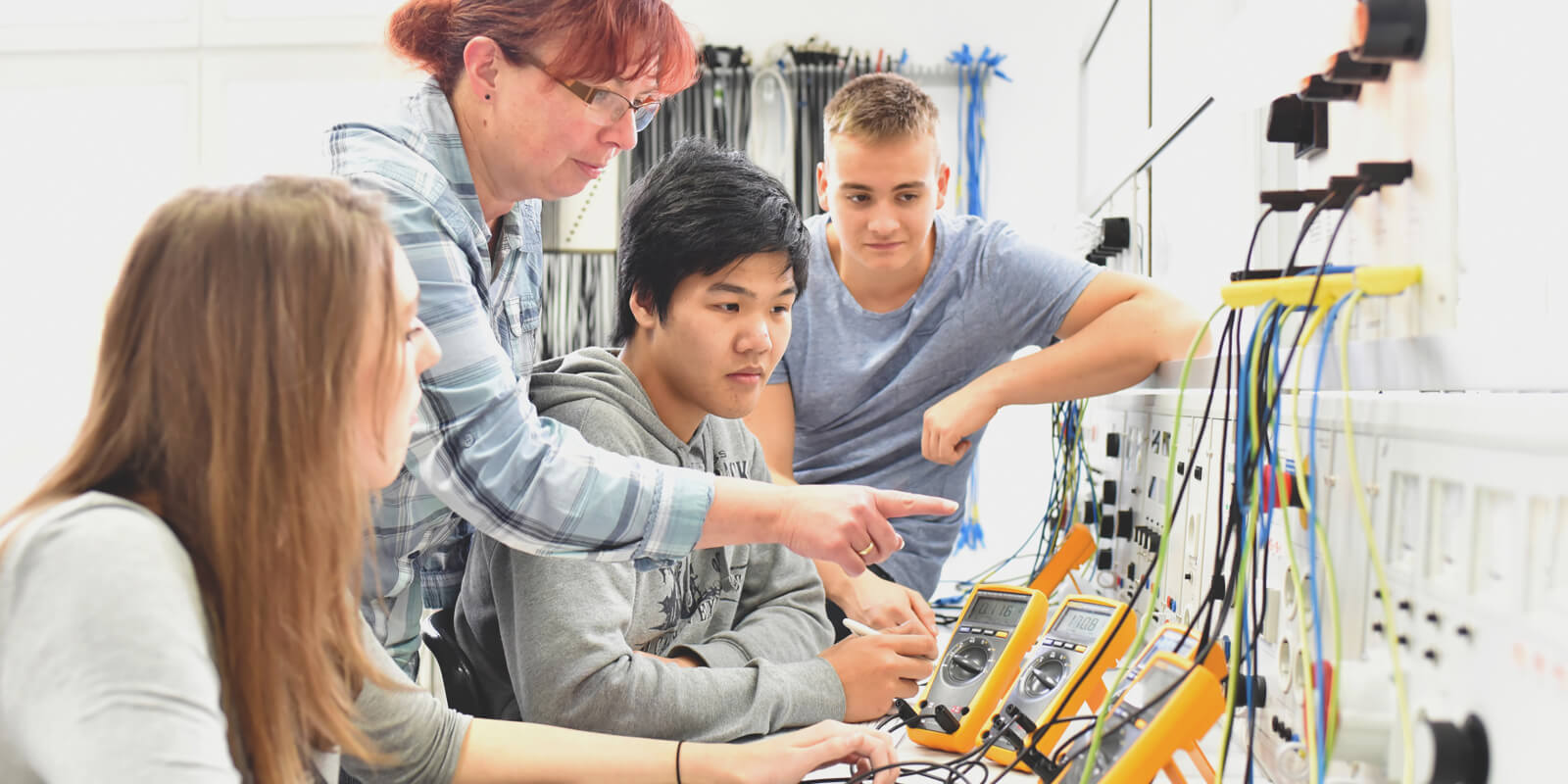
There are many best practices which can be associated with Community Oriented Career & Technical Education (CTE) programs. Three main practices which can apply no matter the demographics of the community have been identified. They are: Advising; Succession Plan; and Community Partnership.
Advising
There is a wealth of academic research which suggests academic advising should serve as fundamental support for students. If implemented correctly, the advisement process allows advisors to extend support to students through academic and career planning. That includes addressing socioeconomic factors (Cueso, 2019) which may influence diploma (K-12) or certificate or degree completion. The advising process should always be tailored to the individual student’s likes, dislikes, abilities, and desires as it relates to the program and course offerings. That is as opposed to a “one size fits all” approach. Doing so encourages a positive, organic relationship between the student and the advisor which will contribute to overall success.
Succession Plan
Unexpected events occur. It is inevitable. Planning for such unexpected events should be an integral part of the best practices conversation. Dual credit courses should feed into both a student’s college credit and certificate or degree program requirements. That is in addition to their knowledge base for their career. Ensuring a transition which is as seamless as possible for the student will impact their outcomes in both short and long term. Developing a thoughtful succession plan allows program administrators and instructors to identify and plan for unexpected events (i.e., change of instructor, change of location, etc.).
Community Partnership
Most successful CTE programs thrive because of their community partnerships. Successful CTE programs carefully identify local partners to assist with the implementation of their programs in various ways.
Think about YOUR Community….
Consider the industries in the local community versus those in other communities with successful CTE programs.
Pay attention to the demographics of the program’s student body and consider those factors when making program improvements.
Naturally, always remember education is not one size fits all!
Learn more about K-12 CTE Pathways dual enrollment programs from Pearson
References:
Cuseo, J. (2019, January). Academic Advisement and Student Retention: Empirical Connections & Systemic Interventions. https://www.shawnee.edu/sites/default/files/2019-01/Academic-advisementv-and-student-retention.pdf
read more