Cytokinesis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (15)
Cytokinesis
The process of dividing the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells, following the division of the nucleus, completing cell division.
M Phase
The M Phase is the cell cycle stage where the nucleus and cytoplasm divide, resulting in two identical daughter cells through mitosis and cytokinesis.
Cell Cycle
A series of stages in a cell's life cycle, including growth, DNA replication, and division, resulting in two daughter cells.
Mitosis
A process in the cell cycle where the nucleus divides, resulting in two identical nuclei, each with the same number of chromosomes as the original nucleus.
Daughter Cells
Genetically identical or varied cells, produced by the division of a parent cell during cell divisions.
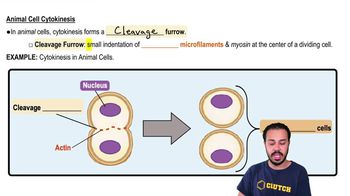
Cleavage Furrow
A groove in the plasma membrane that forms during cytokinesis, leading to the division of the parent cell into two daughter cells.
Metaphase Plate
The equatorial plane where chromosomes align during metaphase before being separated into daughter cells.
FtsZ
A bacterial cytoskeletal protein that forms a contractile ring during binary fission, analogous to the cleavage furrow in eukaryotic cytokinesis.
Bacteriocytoskeleton
A protein-based structure in bacteria that forms a contractile ring, facilitating cell division by binary fission, similar to the cleavage furrow in eukaryotic cytokinesis.
Contractile Ring
A structure composed of actin filaments that forms beneath the plasma membrane during cytokinesis, constricting to divide the parent cell into two daughter cells.
Actin Filaments
Protein structures that form a contractile ring during cytokinesis in animal cells, aiding in the division of the parent cell into two daughter cells.
Cell Plate
A structure formed during plant cell cytokinesis where vesicles coalesce at the center of the cell, leading to the development of a new cell wall, ultimately dividing the cell into two.
Mitotic Spindle
A structure composed of microtubules that segregates chromosomes into daughter cells during mitosis.
Microtubules
Cytoskeletal structures composed of tubulin, essential for cell shape, intracellular transport, and chromosome separation during mitosis.
Microtubule Organizing Center
A cellular structure that nucleates and organizes microtubules, crucial for forming the mitotic spindle during cell division.