Back
BackOxyacids definitions
You can tap to flip the card.
Control buttons has been changed to "navigation" mode.
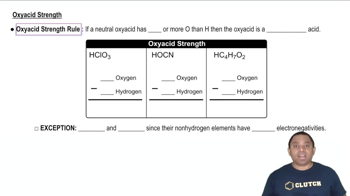
1/15Oxyacids
17. Acid and Base Equilibrium
4 problems
Topic

Jules
Bases
17. Acid and Base Equilibrium
5 problems
Topic

Jules
17. Acid and Base Equilibrium - Part 1 of 4
4 topics 12 problems
Chapter

Jules
17. Acid and Base Equilibrium - Part 2 of 4
6 topics 11 problems
Chapter

Jules
17. Acid and Base Equilibrium - Part 3 of 4
5 topics 11 problems
Chapter

Jules
17. Acid and Base Equilibrium - Part 4 of 4
5 topics 10 problems
Chapter

Jules