- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Which of the statements below regarding the ends of nucleic acids are incorrect?
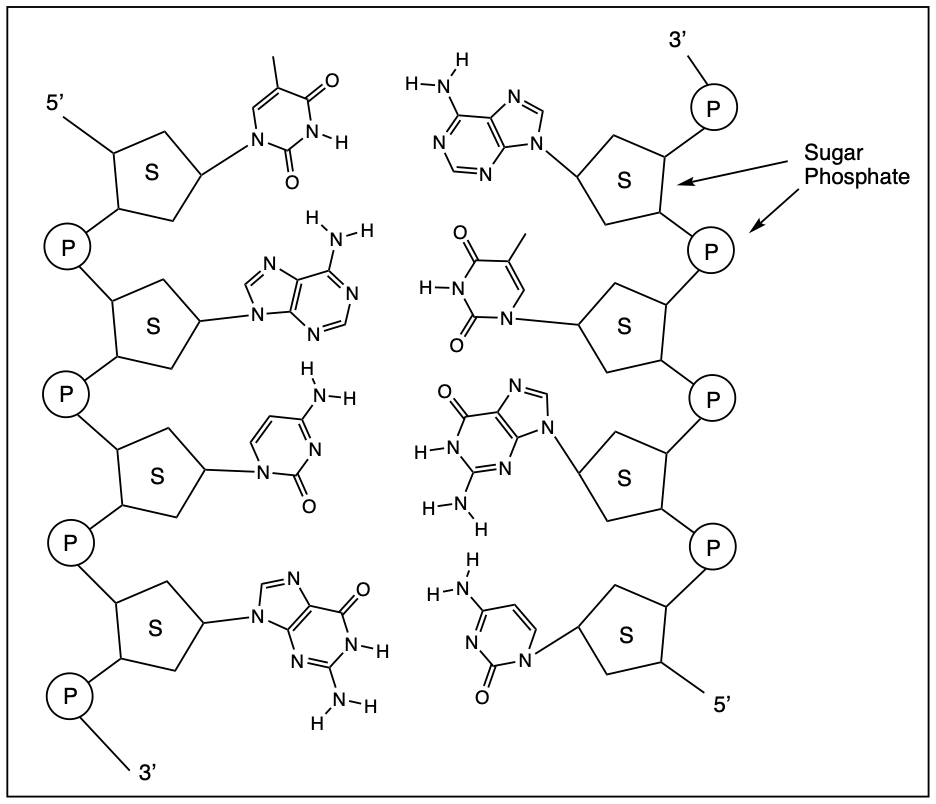
i. The 5' end of a nucleic acid has a free phosphate group attached to the 5' carbon of the sugar.
ii. The 3' end of a nucleic acid has a free hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the 2' carbon of the sugar.
iii. Nucleotides are always added to the 5' end during DNA and RNA synthesis.
iv. The 5' end and 3' end of a nucleic acid are identical in structure.
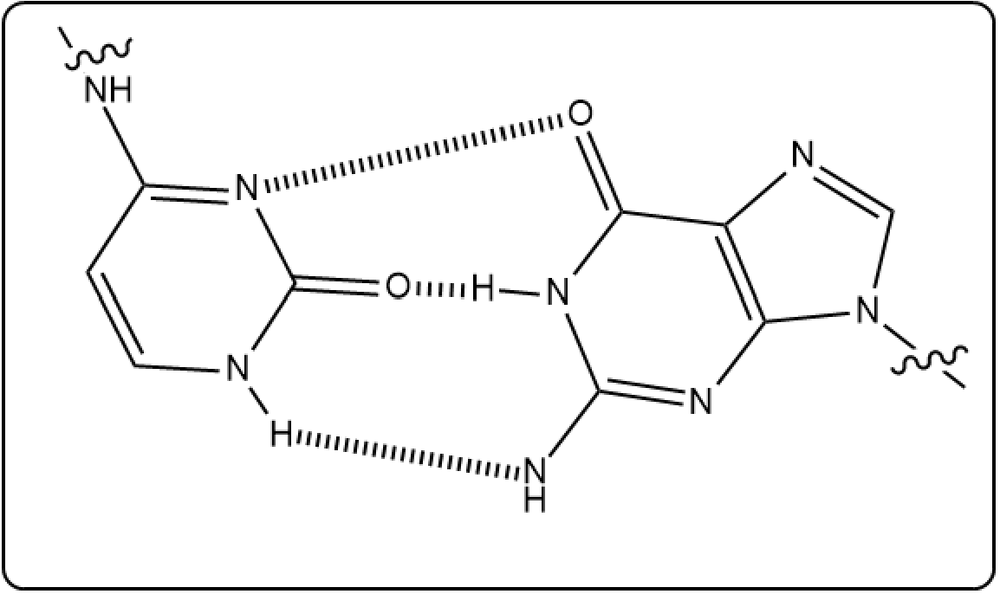
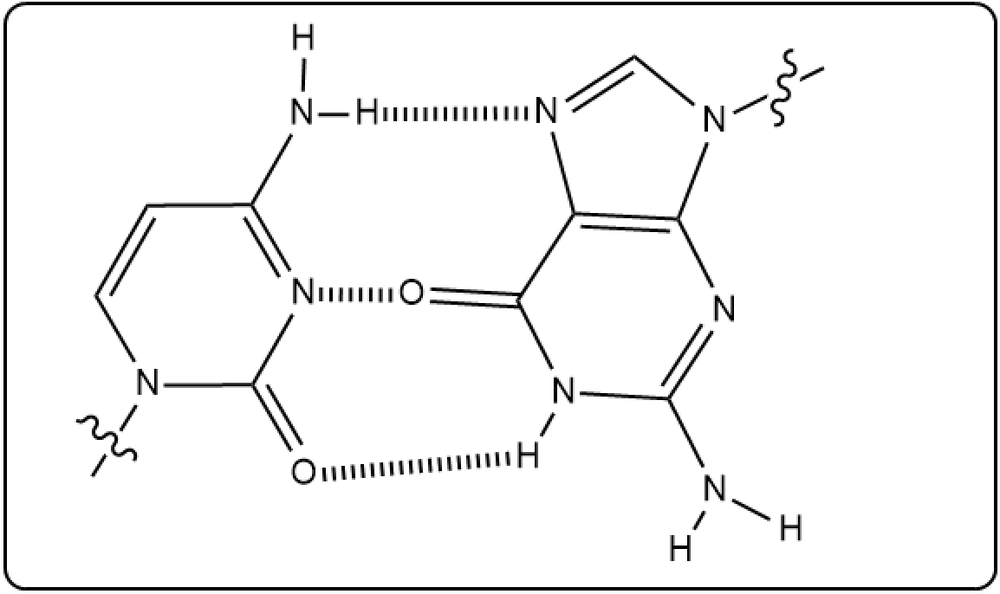
Cytosine and guanine are two base pairs in DNA. Which of the following accurately shows the hydrogen bonding between them?
(i) 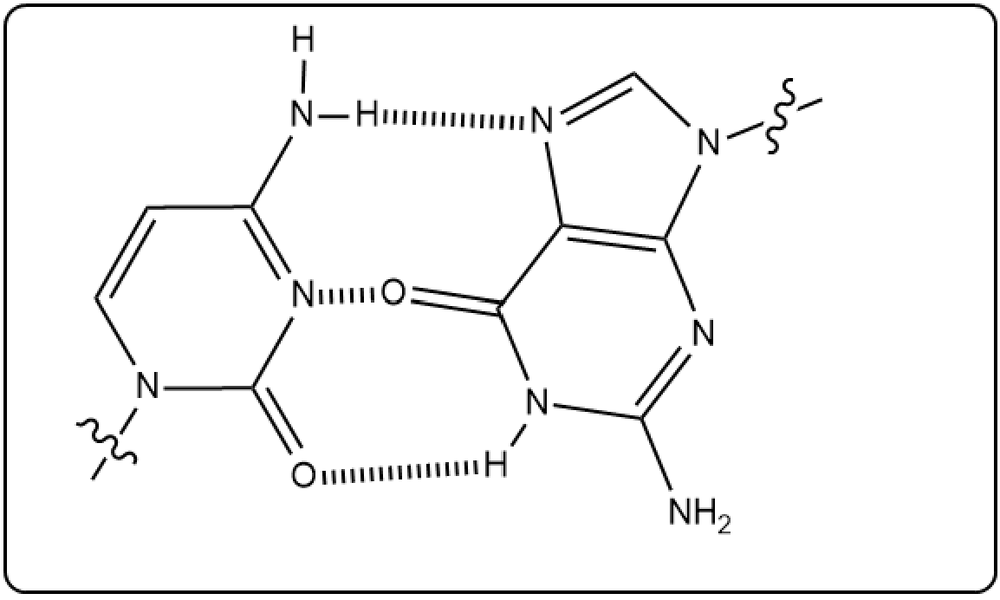
(iii) 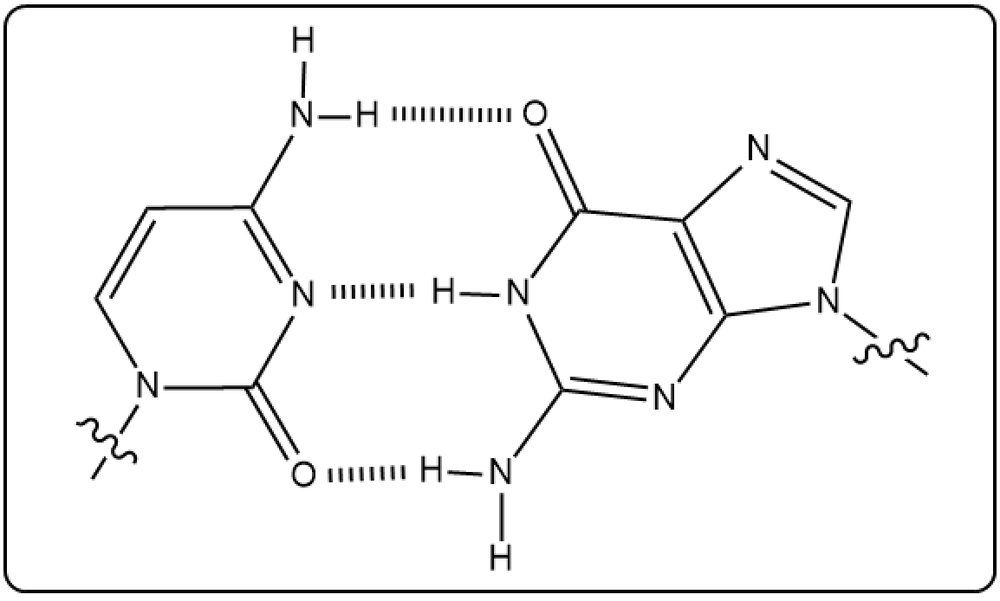
A student analyzed the DNA composition of a sea cucumber. He found out that the sea cucumber's DNA has 16% T and about 34% G. What percentages of A and C would he expect in the sea cucumber's DNA?
What is the complementary DNA base sequence if the original segment is A G T C A C G T T A G C?
Use dotted lines to show the points where hydrogen bonds are formed between the complementary strands of DNA. What is the 5′ to 3′ nucleotide sequence of the following DNA strand?
Which of the following incorrectly describes the characteristic of DNA?
Which of the following incorrectly describes the similarities and differences between the secondary structures of proteins and DNA?
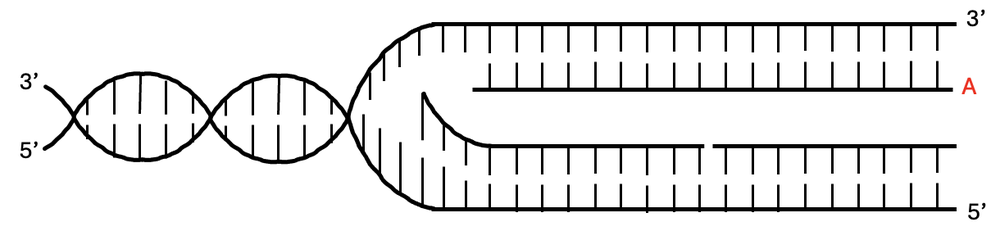
Consider the following DNA replication fork:
Encircle the location of the DNA polymerase on strand A. Determine the direction of the synthesis of strand A.
Which of the following is true about Okazaki fragments and their role in DNA replication?
Which of the following statements describes the process that ensures DNA replication produces identical copies?
Which of the following accurately describes how a gene for a specific protein gets inserted into a plasmid?
Determine which of the given molecules plays a role in DNA replication.
i. RNA polymerase
ii. DNA polymerase
iii. Restriction enzymes
iv. tRNA bonded to codons
v. DNA ligase