- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

3-Methylbut-1-ene gives two substitution products when treated with a low concentration of bromine under irradiation by a sunlamp.
Propose a mechanism to show the formation of these two products.
Determine the carbon in the given radical where the new C—Br bond is most likely to form in the second propagation step of the free radical bromination using NBS.
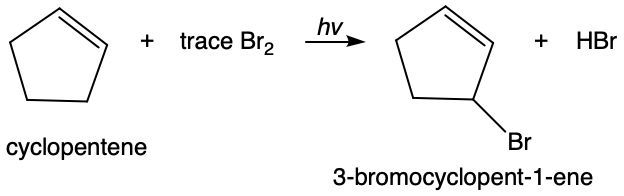
The reaction below proceeds in the presence of light and a small amount of bromine.
Why does cyclopentene react with bromine much faster than cyclopentane, which requires heat to react?
What brominated products are formed in the allylic bromination reaction below? Do not include stereoisomers.

What reagent is required for the bromination of cyclopentene at the allylic position?

Identify the position in the given radical where the new C—Br bond is most likely to form during the second propagation step of the allylic bromination using NBS.

The reaction of 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene with NBS under UV light produces a mixture of two products.

However, the reaction of cyclopentene with NBS only produces one product despite the generation of a resonance-stabilized radical. Explain why this reaction does not yield a second product.
Draw the major product/s when the following organic compound undergoes allylic bromination.