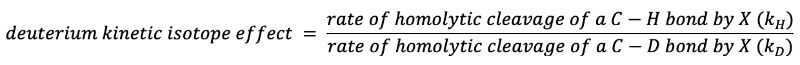- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Without any knowledge of the mechanism for following substitution reaction:

Predict the ratio of the products formed for the reaction (in whole numbers) based on random statistical distribution when iodine (I) replaces hydrogen (H) in isopentane (C5H12).
Determine the ratio of monochlorinated products obtained by chlorination of butane. Assuming that all the hydrogen atoms can be substituted at the same rate.
The equation below defines the deuterium kinetic isotope effect for the halogenation of an alkane (X・ = Cl・ or Br・). Is the deuterium kinetic isotope effect greater in chlorination or bromination?
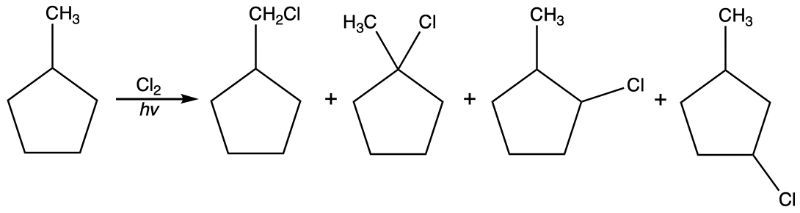
Draw the product(s) of the reaction below. If the reaction is selective, only draw the major product. Otherwise, draw all possible products.

The relative rate of formation of a tertiary, a secondary, and a primary alkyl radical by a chlorine radical is 5 : 3.8 : 1 at room temperature. However, the relative rates for the formation of these radicals decrease when we increase the reaction temperature. Explain this decrease in the degree of regioselectivity.
Determine the expected relative yield of the major product in the following reaction.

Determine whether bromination or chlorination would result in a higher yield of 1-halo-2-methylpropane.
Free radical monochlorination of 3,3-diethylpentane produces 71.69% 2-chloro-3,3-diethylpentane and 28.31% 1-chloro-3,3-diethylpentane. Using the given data, calculate how much easier it is to remove a secondary hydrogen than a primary hydrogen.
Determine the product that will have the highest yield in the reaction below. Explain.