- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Two trucks are moving toward a roundabout. A 2200 kg loaded truck has a speed of 8.60 m/s from north to south. The other truck has a mass of 1980 kg and is headed from east to west with a speed of 19.0 m/s. Determine the magnitude and direction of the total momentum. Take to the north and to the east as +y and +x directions respectively.
Consider a 300 g object that has an initial velocity of 2.0 m/s in the positive x-direction at t = 0 s. If a force of Fx = (6+2t) N, where t is in seconds, is applied to the object in the x-direction between t = 0 s and t = 4 s, how fast will the object be in the x-direction by t = 4 s?
The graph shown below describes the collision of a body. Consider the duration of collision as 21 ms. Find the value of the average collision force experienced by the body.

At what velocity must a unicyclist, with a total mass of 80 kg (including the unicycle), pedal across a tightrope to equal the momentum of a cheetah weighing 60 kg sprinting at a speed of 15 m/s?
A 90 kg bungee jumper descends with a downward momentum of -3600 j kg m/s. Determine the velocity with which he is hurtling toward the ground.
Calculate the magnitude of the momentum of a 33-g butterfly fluttering at 8.5 m/s.
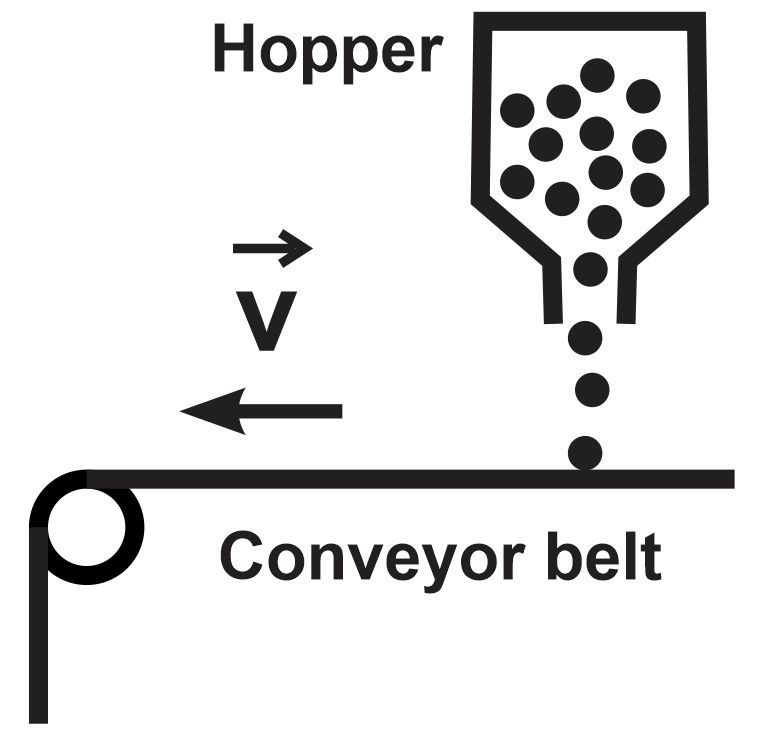
Consider a situation in which a manufacturing assembly line is in operation. In this setup, a conveyor belt maintains a consistent speed of 2.5 m/s, while grains are deposited onto it from a hopper at a rate of 65 kg/s. If the conveyor belt experiences a friction force of 180 N, causing it to slow down, calculate the requisite output power in units of horsepower that the motor experiences over time. This analysis should commence from the instant the grains are initially deposited at t = 0 seconds and extend until 4.0 seconds after the grains commence sliding off the end of the 25-meter-long conveyor belt.