- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A thin light cord is wound around a pulley of diameter 20 cm and mass 1 kg. The pulley is considered to be a thin hoop. Determine the moment of inertia of the pulley around an axis perpendicular to the pulley's plane and passing through the cord.
You make a corner weld between two thin uniform rods of mass 1 kg and length 3 m each. In this situation, the two rods are perpendicular to each other. Determine the moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane of this system and passing through the welding point.
Two tiny iron spheres are welded to a homogenous metallic antenna. The spheres have a mass of 25 g each, whereas the antenna is 1 m long and has a mass of 250 g. Assume that the size of the spheres is small compared to the length of the antenna. Calculate the moment of inertia of this system about a fixed axis parallel to the antenna. The distance between the axis and the antenna is 15 cm.
What will be the moment of inertia for a gate that is 2.6 m tall and 1.1 m wide and weighs 20 kg, about its pivot at one edge, and assuming that the gate's thickness is negligible?
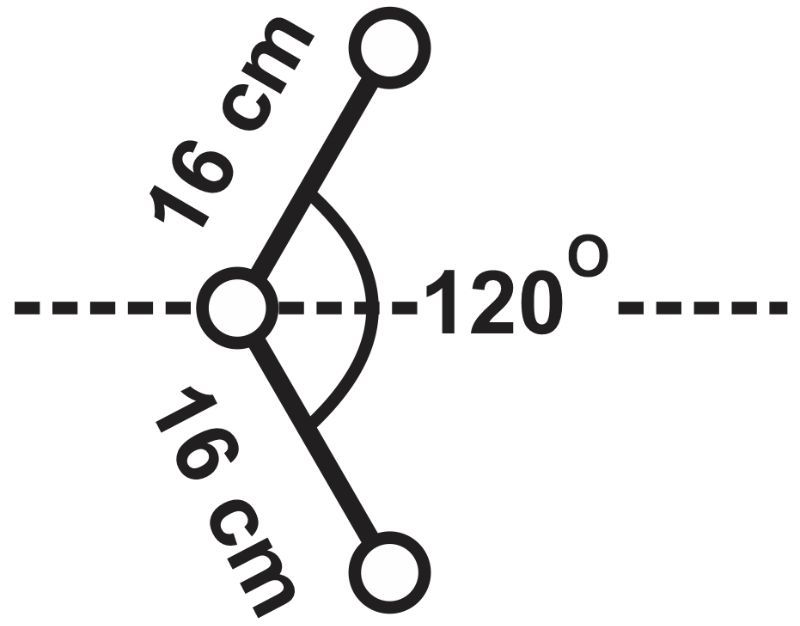
An inventor designs a new kind of boomerang. He attaches three metal balls each of mass 300 g by rigid sticks that have negligible masses as shown in the figure. The balls are arranged in a 'V' shape. Each of the two sides of the boomerang is 16 cm in length and the two sides make an angle of 120° at the vertex. Determine the moment of inertia of the boomerang about an axis that passes through the vertex, lies in the plane the sides of the boomerang are in, and bisects the angle at the vertex.