Textbook Question
Why was it important to include a positive control and a negative control in the PCR analysis?
1360
views

 Freeman 7th Edition
Freeman 7th Edition Ch. 20 - The Molecular Revolution: Biotechnology, Genomics, and New Frontiers
Ch. 20 - The Molecular Revolution: Biotechnology, Genomics, and New Frontiers Problem 15
Problem 15 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

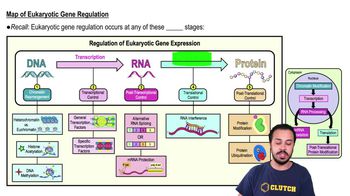
Why was it important to include a positive control and a negative control in the PCR analysis?
How could the research group determine whether a homologous gene for blight resistance exists in the human genome?