Back
BackProblem 1
What do some photosynthetic bacteria use as a source of electrons instead of water?
a. Oxygen (O2)
b. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
c. Organic compounds (e.g., CH3COO−)
d. Nitrate (NO3-)
Problem 2
What are organisms called that use inorganic compounds as electron donors in cellular respiration?
a. Phototrophs
b. Heterotrophs
c. Organotrophs
d. Lithotrophs
Problem 3
Unlike plant cell walls that contain cellulose, bacterial cell walls are composed of ___________.
Problem 4
Evaluate these statements about Koch's postulates, which are used to establish a causative link between a specific microbe and a specific disease. Select True or False for each statement.
T/F The microbe must be present in individuals suffering from the disease and absent from healthy individuals.
T/F The microbe must be isolated and grown in pure culture.
T/F If organisms from the pure culture are injected into a healthy experimental animal, the disease symptoms should appear.
T/F The microbe does not have to be isolated from the experimental animal as long as the disease is present.
Problem 5
What has metagenomic analysis allowed researchers to do for the first time? a. sample organisms from an environment and grow them under defined conditions in the lab b. isolate organisms from an environment and sequence their entire genome c. study organisms that cannot be cultured (grown in the lab) d. identify important morphological differences among species
- What has metagenomic analysis allowed researchers to do for the first time? a. sample organisms from an environment and grow them under defined conditions in the lab b. isolate organisms from an environment and sequence their entire genome c. study organisms that cannot be cultured (grown in the lab) d. identify important morphological differences among species
Problem 5
Problem 6
Biologists often use the term 'energy source' as a synonym for 'electron donor.' Why?
Problem 7
The text claims that the evolution of an oxygen-rich atmosphere paved the way for increasingly efficient cellular respiration and higher growth rates in organisms. Explain.
Problem 9
Streptococcus mutans obtains energy by oxidizing sucrose. This bacterium is abundant in the mouths of Western European and North American children and is a prominent cause of cavities. The organism is virtually absent in children from East Africa, where tooth decay is rare. Propose a hypothesis to explain this observation. Outline the design of a study that would test your hypothesis.
- Streptococcus mutans obtains energy by oxidizing sucrose. This bacterium is abundant in the mouths of Western European and North American children and is a prominent cause of cavities. The organism is virtually absent in children from East Africa, where tooth decay is rare. Propose a hypothesis to explain this observation. Outline the design of a study that would test your hypothesis.
Problem 9
Problem 10
Suppose that you've been hired by a firm interested in using bacteria to clean up organic solvents found in toxic waste dumps. Your new employer is particularly interested in finding cells that are capable of breaking a molecule called benzene into less-toxic compounds. Where would you go to look for bacteria that can metabolize benzene as an energy or carbon source? How would you design an enrichment culture capable of isolating benzene-metabolizing species?
Problem 11
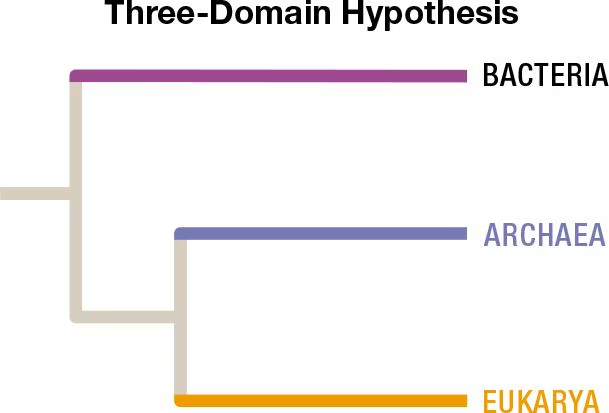
The traditional tree of life (shown above) presents the three domains as distinct, monophyletic lineages. However, other hypotheses propose different views on the relationships among the Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. In particular, the two-domain hypothesis—or eocyte hypothesis—is emerging as a well-supported alternative to the three-domain hypothesis. The eocyte hypothesis, illustrated below, suggests that eukaryotes evolved from eocytes (also known as the Crenarchaeota—a major lineage of the Archaea). Resolving the relationships among these ancient lineages is difficult, but it has profound implications on our understanding of the origin of eukaryotic cells.
Why are Archaea considered a monophyletic group according to the three-domain hypothesis?
a. Because this group includes all organisms except eukaryotes.
b. Because this group includes an ancestral population and all of its descendants.
c. Because all members of this group lack membrane-bound organelles.
d. Because this group evolved after the origin of bacteria.
Problem 12
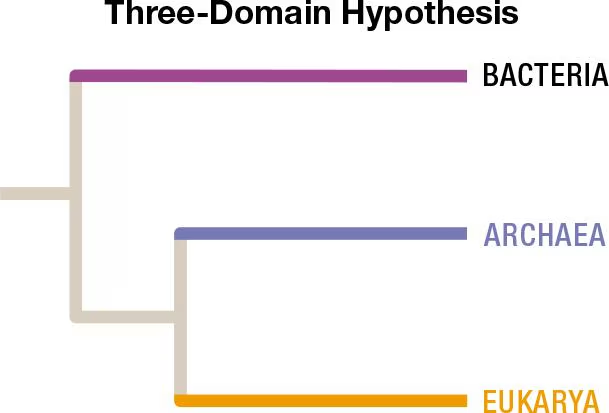
The traditional tree of life (shown above) presents the three domains as distinct, monophyletic lineages. However, other hypotheses propose different views on the relationships among the Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. In particular, the two-domain hypothesis—or eocyte hypothesis—is emerging as a well-supported alternative to the three-domain hypothesis. The eocyte hypothesis, illustrated below, suggests that eukaryotes evolved from eocytes (also known as the Crenarchaeota—a major lineage of the Archaea). Resolving the relationships among these ancient lineages is difficult, but it has profound implications on our understanding of the origin of eukaryotic cells.

The Bacteria and Archaea both include microscopic prokaryotes that lack membrane-bound nuclei. What criteria have led to the classification of these two groups as separate domains?
Problem 13
The traditional tree of life (shown above) presents the three domains as distinct, monophyletic lineages. However, other hypotheses propose different views on the relationships among the Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. In particular, the two-domain hypothesis—or eocyte hypothesis—is emerging as a well-supported alternative to the three-domain hypothesis. The eocyte hypothesis, illustrated below, suggests that eukaryotes evolved from eocytes (also known as the Crenarchaeota—a major lineage of the Archaea). Resolving the relationships among these ancient lineages is difficult, but it has profound implications on our understanding of the origin of eukaryotic cells.

Early ideas on the classification of life recognized all organisms as belonging to one of two fundamental lineages—prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Is this view compatible with either of the hypotheses illustrated here? Explain.
Problem 14
The traditional tree of life (shown above) presents the three domains as distinct, monophyletic lineages. However, other hypotheses propose different views on the relationships among the Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. In particular, the two-domain hypothesis—or eocyte hypothesis—is emerging as a well-supported alternative to the three-domain hypothesis. The eocyte hypothesis, illustrated below, suggests that eukaryotes evolved from eocytes (also known as the Crenarchaeota—a major lineage of the Archaea). Resolving the relationships among these ancient lineages is difficult, but it has profound implications on our understanding of the origin of eukaryotic cells.

Other hypotheses for the tree of life present the Archaea as the ancestors to all other organisms. Sketch a phylogenetic tree that presents Bacteria and Eukarya as more closely related to each other than to Archaea, and that has Archaea as a sister group to Bacteria and Eukarya.
Problem 15
The traditional tree of life (shown above) presents the three domains as distinct, monophyletic lineages. However, other hypotheses propose different views on the relationships among the Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. In particular, the two-domain hypothesis—or eocyte hypothesis—is emerging as a well-supported alternative to the three-domain hypothesis. The eocyte hypothesis, illustrated below, suggests that eukaryotes evolved from eocytes (also known as the Crenarchaeota—a major lineage of the Archaea). Resolving the relationships among these ancient lineages is difficult, but it has profound implications on our understanding of the origin of eukaryotic cells.

Evaluate this statement: According to the two-domain hypothesis, all members of the domain Archaea are prokaryotes and therefore lack membrane-bound nuclei.
Problem 16
The traditional tree of life (shown above) presents the three domains as distinct, monophyletic lineages. However, other hypotheses propose different views on the relationships among the Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. In particular, the two-domain hypothesis—or eocyte hypothesis—is emerging as a well-supported alternative to the three-domain hypothesis. The eocyte hypothesis, illustrated below, suggests that eukaryotes evolved from eocytes (also known as the Crenarchaeota—a major lineage of the Archaea). Resolving the relationships among these ancient lineages is difficult, but it has profound implications on our understanding of the origin of eukaryotic cells.

What other types of evidence or features might be used to ascertain whether the tree of life is best represented according to the three-domain or the eocyte hypothesis?