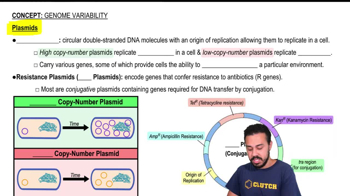
Textbook Question
What does species richness refer to? Select True or False for each statement.
T/Fthe number of species in an area
T/Fthe evenness of species in an area
T/Fthe functional diversity of a species in an area
T/Fthe phylogenetic diversity of species in an area
931
views