- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

True or False: Glucose, ribose, and mannose are the primary monosaccharides produced from the enzymatic breakdown of dietary carbohydrates.
Identify the carbohydrate that undergoes digestion in the mouth.
What are the initial reactant and final product of the glycolysis process?
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is a key intermediate in metabolism and the glycolysis pathway. Which of the following conditions and statements below is correct?
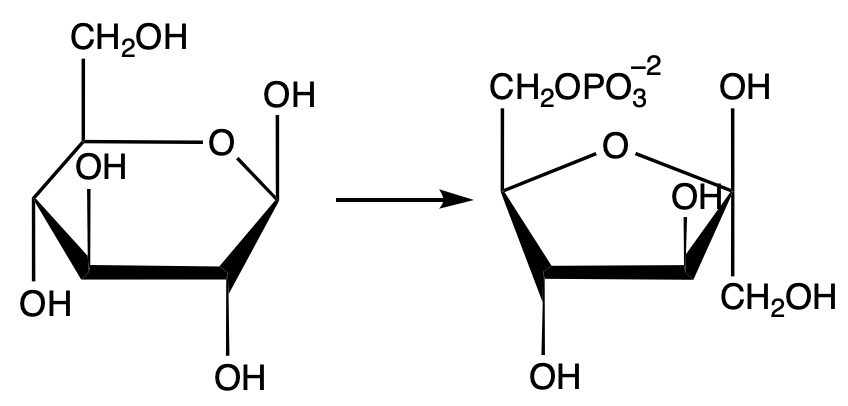
Determine the two (2) kinds of reactions that would transform glucose to fructose 6-phosphate.
How many ATP molecules are consumed or produced during the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in glycolysis?
Give the net output of high-energy molecules for 5 molecules of galactose in glycolysis.
Which of the following statements about the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is/are correct? (Select all that apply.)
I. NAD⁺ is reduced to NADH during the oxidation of pyruvate.
II. The reaction occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
III. Coenzyme A (CoA) is required to form acetyl CoA.
IV. Pyruvate oxidation directly produces ATP.
Which of the sets below depicts the correct pyruvate catabolism products under different conditions?
How much net amount (in terms of mole) of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) can be obtained through the glycolytic pathway starting with 7.0 moles glucose?
How many total moles of ATP (at maximum) are generated from the complete oxidation of 5 moles of acetyl-CoA through the citric acid cycle and subsequent oxidative phosphorylation?
Calculate the number of ATP molecules generated when 7.00 molecules of glucose are fully oxidized to CO2 and H2O.
Which of the following statement/s regarding the molecules used for gluconeogenesis is correct?
I. The primary substrate for gluconeogenesis is glucose obtained from dietary sources, which is then converted back into glucose for storage.
II. Gluconeogenesis is predominantly active during the fed state when glucose levels are high, to further increase blood glucose.
III. Gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in liver cells during high-intensity exercise to directly convert muscle glycogen into glucose.
IV. Amino acids are key substrates in gluconeogenesis, helping to produce glucose when carbohydrate intake is low.
Which of the following statements about the pathway of gluconeogenesis and the role of pyruvate is correct?
I. Pyruvate is converted directly into glucose during gluconeogenesis.
II. Gluconeogenesis converts pyruvate into glucose in the liver, using ATP and GTP to reverse the glycolytic pathway.
III. During gluconeogenesis, pyruvate is directly converted into lactate without an intermediary step.
IV. The conversion of pyruvate to glucose in gluconeogenesis is an energy-neutral process, requiring no additional ATP.
True or false:
i. It is important for muscle cells to export lactate into the bloodstream during heavy exercise to prevent the accumulation of lactate in the muscles.
ii. The kidneys convert lactate back into glucose, which helps sustain energy production.