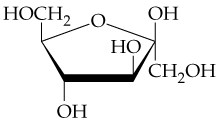
The cyclic structure of D-idose, an aldohexose, is shown in the margin. Convert this to the straight-chain Fischer projection structure.

In the monosaccharide hemiacetal shown below number all the carbon atoms, identify the anomeric carbon atom, and identify it as the α or β anomer.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Monosaccharides

Hemiacetal Formation
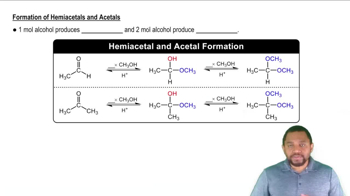
Anomeric Carbon
Draw the structure that completes the mutarotation reaction between the two cyclic forms of (a) galactose and (b) fructose.
a.
Draw the structure that completes the mutarotation reaction between the two cyclic forms of (a) galactose and (b) fructose.
b.
L-Fucose is one of the naturally occurring L monosaccharides. It is present in the short chains of monosaccharides by which blood groups are classified. Compare the structure of L-fucose shown in the margin with the structures of α- and β-D-galactose and answer the following questions.
d. "Fucose” is a common name. Is 6-deoxy-L-galactose a correct name for fucose? Why or why not?
Draw the structure of the α and β anomers that result from the reaction of methanol and ribose. Are these compounds acetals or hemiacetals?
How would you classify the link between the monosaccharides in cellobiose?
