- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Find the tension in cords A, B, and C for an object with weight w suspended by cords as shown below.

A crane lifts a slab using two steel cables attached to its upper edges. The tension in each cable is equal to 0.80 of the slab's weight. If the two cables have the same angle relative to the vertical, determine the value of this angle that makes the tension in the cable equal to 0.8 of the slab's weight.
Thepractice of slowly and gently pushing on a fractured or dislocated body part is known as traction. Often, ropes, pulleys, and weights are used for it. Consider a traction setup as shown in the figure. Assuming the pulleys are frictionless calculate the tension force in the rope that supports the leg.

Two traffic lights are installed at an intersection. One is put in place for traffic and weighs 12 kg, while the other is installed for pedestrians and weighs 8.0 kg. The figure shows the two traffic lights hanging and connected using a highly flexible and lightweight cable.Determine the tension and angle (θ1) of the first cableif the center cable is adjusted to be perfectly horizontal.

At a carnival, a challenge is set up for two people. To win the challenge they must pull a rectangular box to the finish line but both of them should have equal pulls. The angle between the two ropes tied to the box is 30 degrees. If the friction force on the box is 970 N, determine how much force each person must use to pull the box at a constant 3.0 m/s.

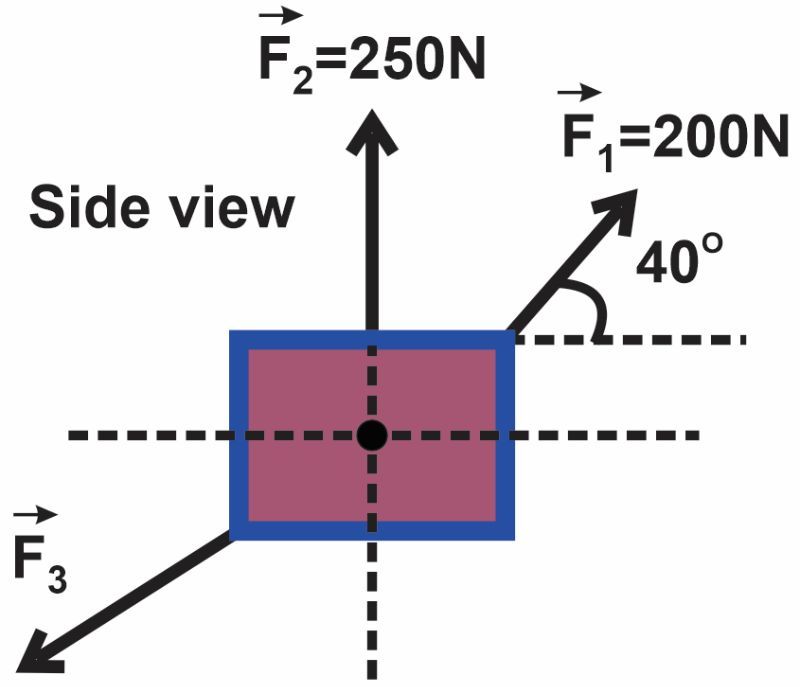
A box is being pulled by three ropes as illustrated below. Given the known forces F1 = 200 N and F2 = 250 N, calculate the magnitude and direction of F3 necessary to maintain equilibrium.
.
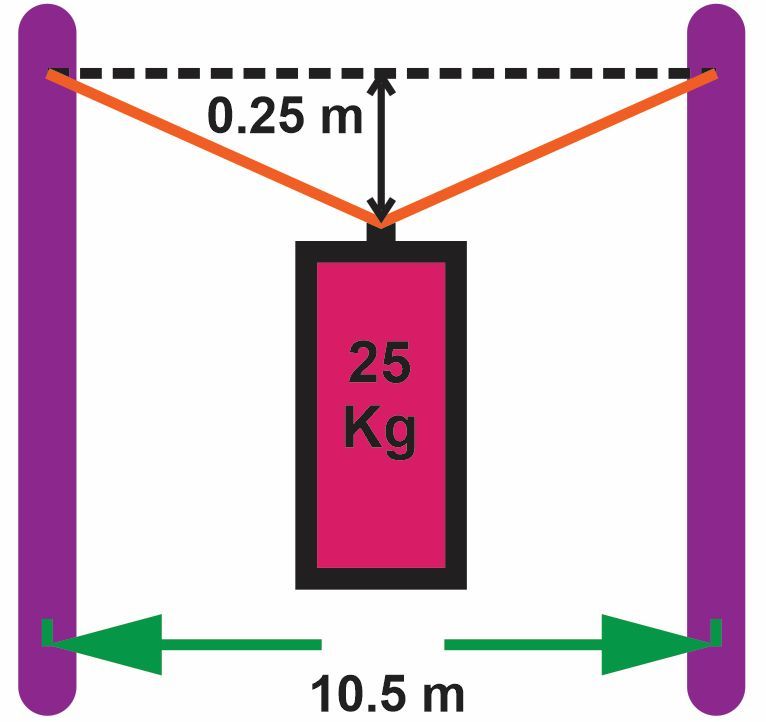
Two lamp posts are positioned 10.5 m apart on a street. A decorative sign of mass 25 kg is to be hung between these posts on a wire, with the goal of having the wire sag by 0.25 m at its midpoint to create an aesthetic droop. Determine the magnitude of the tension in the wire that must be exerted to keep the sign in the desired position.