What does it mean to say that a life cycle is gametophyte dominant versus sporophyte dominant?

Explain the difference between homosporous and heterosporous plants. Where are the microsporangium and megasporangium found in a tulip? What happens to the spores that are produced by these structures?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Homosporous vs. Heterosporous Plants

Microsporangium and Megasporangium
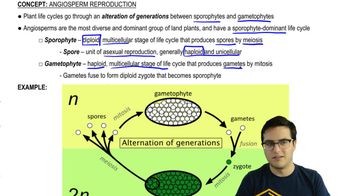
Fate of Spores

Soils, water, and the atmosphere are major components of the abiotic (nonliving) environment. Describe how green plants affect the abiotic environment in ways that are advantageous to humans.
The evolution of cuticle presented plants with a challenge that threatened their ability to live on land. Describe this challenge, and explain why stomata represent a solution. Compare and contrast stomata with the pores found in liverworts.
Angiosperms such as grasses, oaks, and maples are wind pollinated. The ancestors of these subgroups were probably pollinated by insects, however. As an adaptive advantage, why might a species 'revert' to wind pollination? (Hint: Think about the costs and benefits of being pollinated by insects versus wind.) Why is it logical to observe that wind-pollinated species usually grow in dense stands containing many individuals of the same species? Why is it logical to observe that in wind-pollinated deciduous trees, flowers form very early in spring—before leaves form?
You have been hired as a field assistant for a researcher interested in the evolution of flower characteristics in orchids. Design an experiment to determine whether color, size, shape, scent, or amount of nectar is the most important factor in attracting pollinators to a particular species. Assume that you can change any flower's color with a dye and that you can remove petals or nectar stores, add particular scents, add nectar by injection, or switch parts among species by cutting and gluing.
