Carbohydrates exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
Monosaccharides
Single carbohydrate units, such as glucose.
What is the most abundant carbohydrate?
Glucose
Oligosaccharides
Carbohydrates with 2-10 linked monosaccharide units.
What type of bond links monosaccharides together?
Glycosidic bond
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates with more than 10 linked monosaccharide units.
What reaction is needed to break down polysaccharides?
Hydrolysis
Dehydration synthesis
Reaction that links monosaccharides together, forming polysaccharides.
What is the function of cellulose in plants?
Structural support in plant cell walls.
Chitin
A structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans.
What is the primary energy storage polysaccharide in animals?
Glycogen
Starch
An energy storage polysaccharide in plants.
What is the chemical formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
Saccharides
Another term for carbohydrates, derived from the Greek word for sugars.
What is the main function of glycogen in animals?
Energy storage
Cellulose
A polysaccharide used for structural support in plants.
What is the prefix meaning 'many' in polysaccharides?
Poly
Hydrolysis
Reaction that breaks down polysaccharides into monosaccharides.
What is the prefix meaning 'one' in monosaccharides?
Mono
Glycosidic bond
Covalent bond linking monosaccharides together.
What is the primary structural polysaccharide in animals?
Chitin
Energy storage
One of the main functions of carbohydrates, exemplified by starch and glycogen.
What is the prefix meaning 'few' in oligosaccharides?
Oligo
Structural support
One of the main functions of carbohydrates, exemplified by cellulose and chitin.
What is the process called that forms glycosidic bonds?
Dehydration synthesis
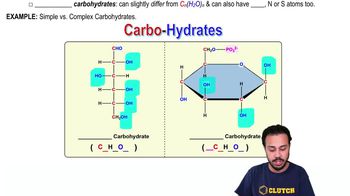
Complex carbohydrates
Carbohydrates that do not fit the simple chemical formula Cn(H2O)n and may contain other atoms like phosphorus, nitrogen, or sulfur.
What is the main function of starch in plants?
Energy storage
Simple carbohydrates
Carbohydrates that fit the chemical formula Cn(H2O)nexactly, such as glucose.
What is the role of peptidoglycan in bacteria?
Structural support in bacterial cell walls.
What does the term 'saccharide' mean?
Sugar