Back
BackSimple and Facilitated Diffusion exam
Terms in this set (26)
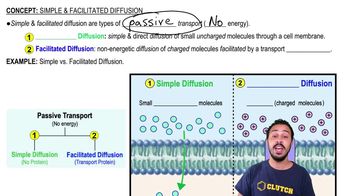
Simple Diffusion
Direct diffusion of small uncharged molecules through the cell membrane without the help of membrane proteins.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport of charged molecules across the membrane with the help of transport proteins.
Passive Transport
Movement of molecules across the cell membrane without the need for energy input.
What is the main difference between simple and facilitated diffusion?
Simple diffusion does not require transport proteins, while facilitated diffusion does.
Concentration Gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a space.
What type of molecules does simple diffusion transport?
Small uncharged molecules.
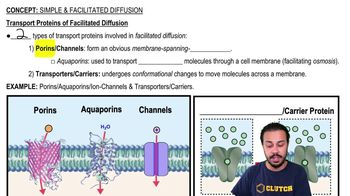
Transport Proteins
Proteins that assist in the movement of molecules across the cell membrane in facilitated diffusion.
Porins
Transport proteins that form membrane-spanning tunnels to allow molecules to pass through.
Carriers
Transport proteins that undergo conformational changes to move molecules across the membrane.
What role do aquaporins play in facilitated diffusion?
They specifically transport water molecules across the cell membrane, facilitating osmosis.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
What is required for facilitated diffusion to occur?
Transport proteins such as porins and carriers.
Energy Requirement
Neither simple diffusion nor facilitated diffusion requires energy input.
What type of molecules does facilitated diffusion typically transport?
Charged molecules (ions).
Membrane-Spanning Tunnel
A structure formed by porins to allow molecules to pass through the membrane.
What is the function of ion channels in facilitated diffusion?
They allow ions to move through the membrane-spanning tunnels created by porins.
Conformational Change
A change in the shape of a carrier protein that allows it to transport molecules across the membrane.
What is the natural tendency of molecules in passive transport?
To move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
Cellular Homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal conditions in a cell.
What is the role of transport proteins in facilitated diffusion?
To assist charged molecules in crossing the cell membrane.
Aquaporins
Specialized porins that facilitate the transport of water molecules.
What is the main characteristic of passive transport?
It requires no energy input.
Ion Channels
Channels that allow ions to pass through the cell membrane in facilitated diffusion.
What happens to carrier proteins during facilitated diffusion?
They undergo conformational changes to transport molecules.
What is the role of passive transport in cells?
To maintain cellular homeostasis and nutrient absorption.
What type of transport is facilitated diffusion?
A type of passive transport.