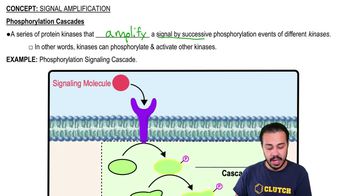
When the doctor listened to Janet's heart, he heard 'lub-hiss, lub-hiss' instead of the normal 'lub-dup' sounds. The hiss is most likely due to _________ . (Explain your answer.)
a. A defective atrioventricular (AV) valve
b. A damaged pacemaker (SA node)
c. A defective semilunar valve
d. High blood pressure