Textbook Question
Complete this map, which presents some major concepts from this chapter.
952
views

 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System
Ch. 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Problem 2
Problem 2 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

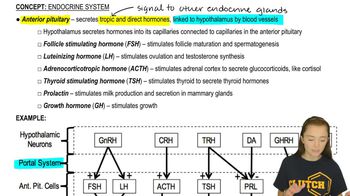

The body is able to maintain a relatively constant level of thyroid hormone in the blood because
a. Thyroid hormone stimulates the pituitary to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
b. Thyroid hormone inhibits the secretion of TSH-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus.
c. TRH inhibits the secretion of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland.
d. Thyroid hormone stimulates the hypothalamus to secrete TRH.