
 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 16 Microbial Life: Prokaryotes and Protists
Ch. 16 Microbial Life: Prokaryotes and Protists Problem 11
Problem 11The bacteria that cause tetanus can be killed only by prolonged heating at temperatures considerably above boiling. This suggests that tetanus bacteria
a. Have cell walls containing peptidoglycan.
b. Secrete endotoxins.
c. Are autotrophic.
d. Produce endospores.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Endospores

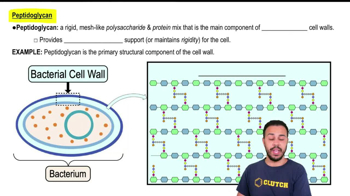
Peptidoglycan
Autotrophic vs. Heterotrophic

What characteristic distinguishes true multicellularity from colonies of cells?
Chlamydomonas is a unicellular green alga. How does it differ from a photosynthetic bacterium, which is also single-celled? How does it differ from a protozoan, such as an amoeba? How does it differ from larger green algae, such as sea lettuce (Ulva)?
Which of the following experiments could test the hypothesis that bacteria cause ulcers in humans? (Assume each experiment includes a control group.) Explain what evidence would be provided by the results of the experiment.
a. Identify the microbes found in the stomachs of ulcer patients.
b. Treat a group of ulcer patients with antibiotics.
c. Place a group of ulcer patients on a strict low-acid diet.
d. Obtain stomach fluid from ulcer patents and feed it to mice.
In a process known as 'coral bleaching,' high water temperatures cause corals to expel the dinoflagellates that normally reside within their cells. How might coral bleaching affect coral reefs?
Probiotics, foods and supplements that contain living microorganisms, are thought to cure problems of the digestive tract by restoring the natural balance of its microbial community. Sales of these products total billions of dollars a year. Explore the topic of probiotics and evaluate the scientific evidence for their beneficial effects. A good starting point is the website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, which regulates advertising claims of health benefits of dietary supplements. U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, www.fda.gov/food/dietary-supplements.