Brachiopoda is a phylum within the Lophotrochozoa. Even though they are not closely related to bivalve mollusks (such as clams or mussels), brachiopods look and act like bivalve mollusks. Specifically, brachiopods suspension feed, secrete calcium carbonate shells with two valves that hinge together in some species, and attach to rocks or other hard surfaces on the ocean floor. How is it possible for brachiopods and bivalves to be so similar if they did not share a recent common ancestor?

About a third of insect species measured are in decline, meaning that their populations are shrinking due to habitat destruction, pollution, and other factors. Predict how this change affects the bee pollination of crops such as apples and almonds.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Pollination

Ecosystem Services
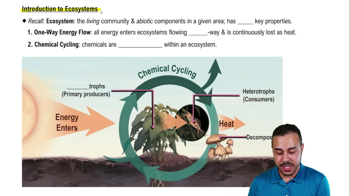
Biodiversity and Resilience

A team of 102 scientists spent a year surveying a small area of the San Lorenzo rain forest in Panama to count the number of species of arthropods living there. After collecting 129,494 specimens—using nets, traps, shovels, tree-climbing harnesses, helium balloons, and other creative gear—it took the team eight years to sort and identify the arthropods. Which of the following nested groups best describes the taxonomic context for the San Lorenzo project?
a. Animalia > Bilateria > Arthropoda > Ecdysozoa
b. Protostomia > Lophotrochozoa > Ecdysozoa > Arthropoda
c. Arthropoda > Protostomia > Ecdysozoa > Bilateria
d. Bilateria > Protostomia > Ecdysozoa > Arthropoda
A team of 102 scientists spent a year surveying a small area of the San Lorenzo rain forest in Panama to count the number of species of arthropods living there. After collecting 129,494 specimens—using nets, traps, shovels, tree-climbing harnesses, helium balloons, and other creative gear—it took the team eight years to sort and identify the arthropods. Rather than measuring the entire 6000-hectare (ha) forest, the researchers sampled arthropod diversity by intensively collecting as many arthropods as they could in 12 plots that measured 20 m × 20m square. If 1 ha=10,000 m², how many hectares of forest did they sample in all?
a. 20 m×20 m×12=4800 ha
b. 4800 m²×10,000 m²/1 ha=48,000,000 ha
c. 20 m×20 m=400 ha
d. 4800 m² x ha/10,000 m² = 0.48 ha
A team of 102 scientists spent a year surveying a small area of the San Lorenzo rain forest in Panama to count the number of species of arthropods living there. After collecting 129,494 specimens—using nets, traps, shovels, tree-climbing harnesses, helium balloons, and other creative gear—it took the team eight years to sort and identify the arthropods. The graph below shows some of the data for the major arthropod groups collected. Notice that the scale on the y-axis is logarithmic to make both small and large numbers legible on the same graph. For example, there are about 400 species of spiders but only 40 species of bees.
About how many arthropods were found in total?
About what percentage of these were beetles?
