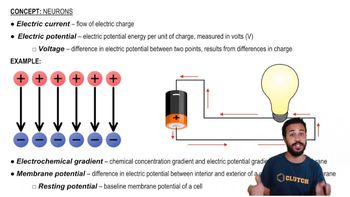
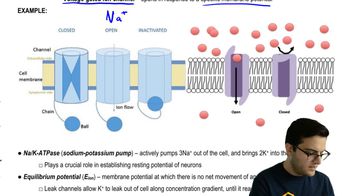
Why is memory thought to involve changes in particular synapses?
a. At some synapses, more neurotransmitters are released after learning takes place.
b. At some synapses, a different type of neurotransmitter is released after learning takes place.
c. When researchers stimulated certain neurons electrically, individuals replayed memories.
d. When researchers changed synapses in the brains of patients during surgery, the patients' memories changed.