Propose a hypothesis to explain how self-reactive B cells are identified and eliminated during maturation.

<Image>
In developed countries, an enormous change has occurred within the human body over the past century—the loss of parasitic worms. Due to improvements in sanitation, roundworms that have inhabited human intestines (such as the hookworm above) and challenged our immune system for millions of years are no longer a threat. Does the end of this long-term relationship come at a cost?
Pattern-recognition receptors have been identified that recognize worm products. Explain how these receptors are used to activate the adaptive immune response most appropriate for worm infection.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
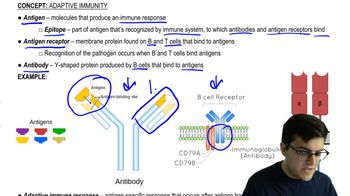
Key Concepts
Pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs)

Adaptive immune response
Immune system adaptation to parasitic worms

<Image>
In developed countries, an enormous change has occurred within the human body over the past century—the loss of parasitic worms. Due to improvements in sanitation, roundworms that have inhabited human intestines (such as the hookworm above) and challenged our immune system for millions of years are no longer a threat. Does the end of this long-term relationship come at a cost?
What is the hygiene hypothesis? What correlation does it attempt to explain?
<Image>
In developed countries, an enormous change has occurred within the human body over the past century—the loss of parasitic worms. Due to improvements in sanitation, roundworms that have inhabited human intestines (such as the hookworm above) and challenged our immune system for millions of years are no longer a threat. Does the end of this long-term relationship come at a cost?
Explain how the adaptive and innate immune responses work together to defend the human body against infection by parasitic worms.
<Image>
In developed countries, an enormous change has occurred within the human body over the past century—the loss of parasitic worms. Due to improvements in sanitation, roundworms that have inhabited human intestines (such as the hookworm above) and challenged our immune system for millions of years are no longer a threat. Does the end of this long-term relationship come at a cost?
Parasitic worms modulate their host's immune response by inducing the proliferation of regulatory T cells. What role do these cells play in the adaptive immune response? How could this effect on regulatory T cells be linked to the hygiene hypothesis?
<Image>
In developed countries, an enormous change has occurred within the human body over the past century—the loss of parasitic worms. Due to improvements in sanitation, roundworms that have inhabited human intestines (such as the hookworm above) and challenged our immune system for millions of years are no longer a threat. Does the end of this long-term relationship come at a cost?
The roundworm Heligmosomoides polygyrus is a natural intestinal parasite of mice, and it offers an excellent model of the immunology of worm infections in humans. Scientists evaluated the impact of parasitic roundworms on immune disorders using mice prone to developing type 1 diabetes mellitus. Five-week-old mice were infected with H. polygyrus (Hp). Two weeks later, half of the mice were cured of the infection (Rx). When the mice were 40 weeks old, scientists calculated the percentage of mice that developed diabetes in both groups: those exposed to roundworms and those in uninfected control groups (** means P<0.01). What two conclusions are supported by the results shown below?
<Image>
In developed countries, an enormous change has occurred within the human body over the past century—the loss of parasitic worms. Due to improvements in sanitation, roundworms that have inhabited human intestines (such as the hookworm above) and challenged our immune system for millions of years are no longer a threat. Does the end of this long-term relationship come at a cost?
There is a strong association between the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in parents and their children. If you were a physician, would you ask parents who have type 1 diabetes to intentionally infect their children with intestinal worms? What additional information would you need to make this decision?
