Explain why decomposition rates in a field in Nebraska would differ from the decomposition rates in a field in the Amazon. How do decomposers regulate nutrient availability in ecosystems?

Suppose that record snows blanket your campus this winter. Your friend says this is proof that global warming isn't really occurring. What is the flaw in your friend's logic?
a. The average temperature of the Earth is not actually increasing.
b. Global warming refers to temperatures, but snow is a type of precipitation.
c. While the average global temperature is increasing, local temperatures and precipitation (weather) will vary.
d. Your friend is confusing global warming and global climate change.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Global Warming
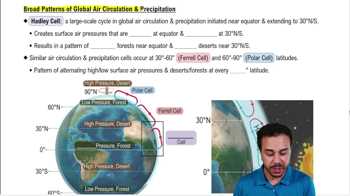
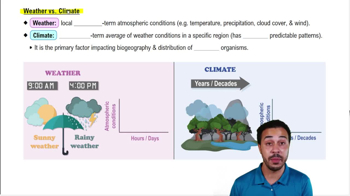
Weather vs. Climate
Global Climate Change

Why are the open oceans nutrient poor? Why are coastal areas and intertidal habitats relatively nutrient rich?
Explain why it is more energy efficient (in terms of the amount of total NPP required) to eat a pound of tofu (bean curd) than a pound of hamburger.
During the Carboniferous period, plant growth was extensive but rates of decomposition slowed (probably due to the formation of vast, oxygen-poor swamp habitats). As a result, large amounts of biomass accumulated in terrestrial environments (much of this biomass is now coal). The fossil record indicates that atmospheric oxygen increased, atmospheric carbon dioxide decreased, and global temperatures dropped. Explain why.
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
Which of the following biomes typically has the highest net primary productivity?
a. Temperate forest
b. Tropical dry forest
c. Tropical grassland
d. Tropical wet forest
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
Select True or False for each statement about the effects of clear-cutting on the Amazon rain forest, then explain your reasoning.
T/F Nutrient export is likely to decline.
T/F Atmospheric CO2 is likely to decline.
T/F Soil moisture is likely to decline.
T/F Species diversity is likely to decline.
