Textbook Question
Use arrows to show electron pairing in the valence p subshell of
a. Sulfur
b. Bromine
c. Silicon
1466
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
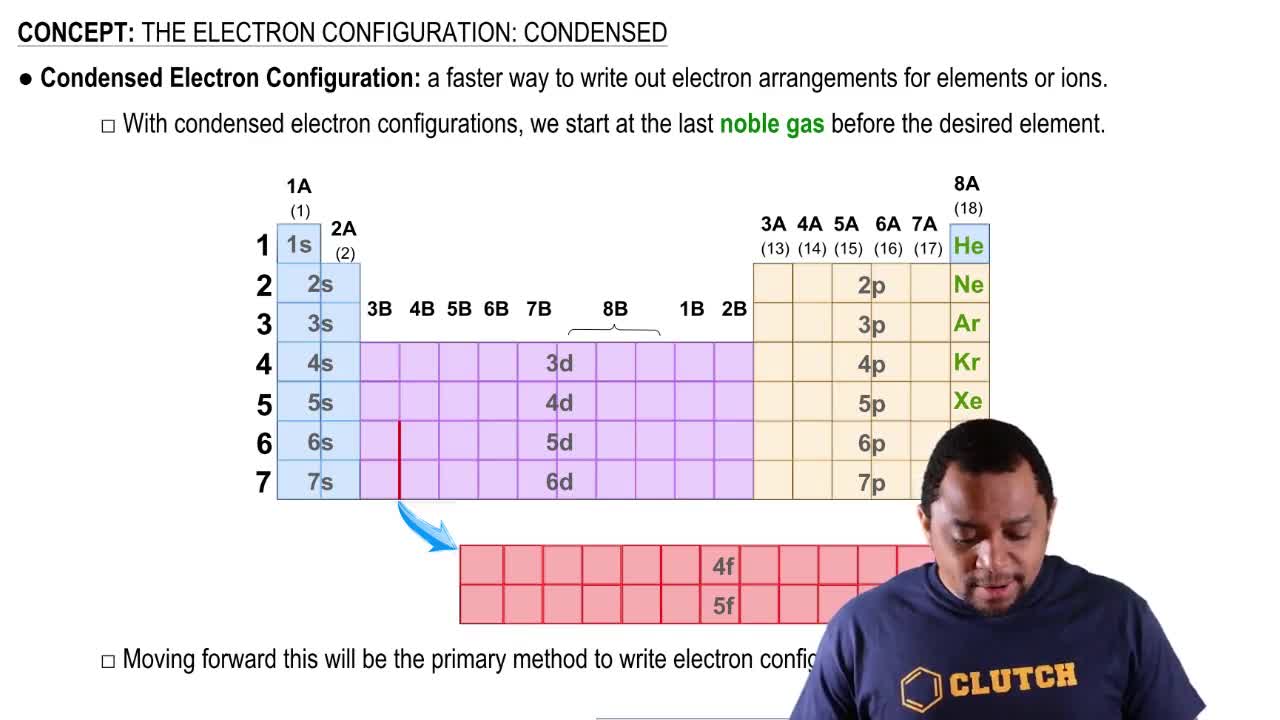
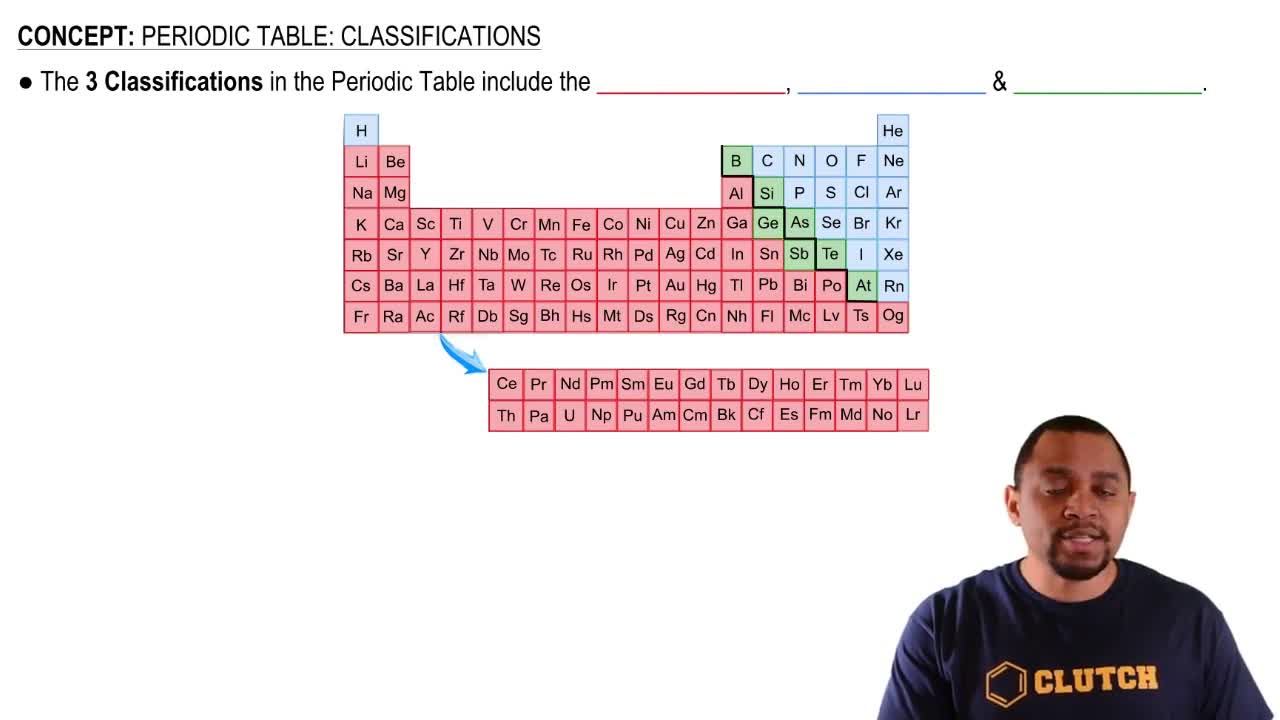
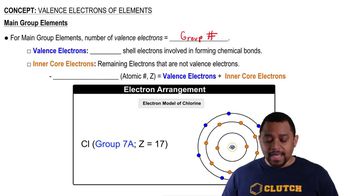
Use arrows to show electron pairing in the valence p subshell of
a. Sulfur
b. Bromine
c. Silicon
What is the mass (in amu and in grams) of a single atom of Carbon-12?
What is the mass (in grams) of 6.02 × 1023 atoms of Carbon-12?
What is wrong with the following electron configurations?
a. Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10
b. N 1s2 2p5
c.
d.
Look again at the trends illustrated in Figures 2.3 and 2.4.
a. How do the peaks/valleys correlate with locations in the periodic table?
b. Are there other chemical properties that also exhibit periodic trends? What are they?
<IMAGE>