Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
The mucosa of the esophagus, pharynx, and oral cavity contains simple squamous epithelium to protect it from abrasion.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
The mucosa of the esophagus, pharynx, and oral cavity contains simple squamous epithelium to protect it from abrasion.
Match the following terms with the correct definition.
__Chief cells
__Parietal cells
__Gastrin
__Pyloric sphincter
__Diffuse neuroendocrine (DNES) cells
__Gastroesophageal sphincter
__Pepsin
__Chyme
a. Hormone that stimulates multiple digestive processes
b. Enzyme that begins protein digestion
c. Produce acid and intrinsic factor
d. Liquid produced as a result of stomach churning
e. Produce pepsinogen
f. Cells in gastric glands that produce hormones
g. Controls passage of bolus from esophagus to stomach
h. Controls passage of stomach contents to duodenum
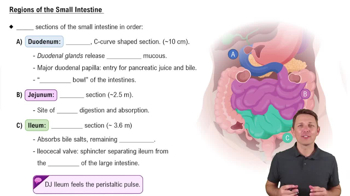
The common hepatic duct and main pancreatic duct enter into the:
a. Pyloric sphincter
b. Duodenum
c. Ileum
d. Cecum
Trace the pathway that food takes through the entire alimentary canal, from the oral cavity to the anal canal.
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
The exocrine cells of the pancreas and salivary glands are islet cells.
Which of the following statements about accessory organ secretions is not true?
a. Hepatocytes produce bile, which drains out of the liver via the common hepatic ducts.
b. Saliva contains secretory IgA and lysozyme, which play an important role in preventing the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity.
c. Pancreatic juice contains digestive enzymes and bicarbonate ions to neutralize the acidic chyme.
d. The gallbladder produces bile, which drains out of the gallbladder via the cystic duct.