Textbook Question
A human's internal organs are protected mainly by the
a. Hydrostatic skeleton.
b. Axial skeleton.
c. Exoskeleton.
d. Appendicular skeleton.
1699
views


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
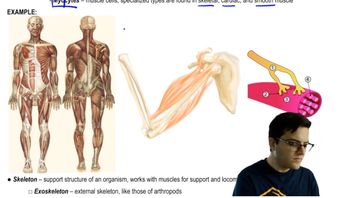


A human's internal organs are protected mainly by the
a. Hydrostatic skeleton.
b. Axial skeleton.
c. Exoskeleton.
d. Appendicular skeleton.
Arm muscles and leg muscles are arranged in antagonistic pairs. How does this affect their functioning?
a. It provides a backup if one of the muscles is injured.
b. One muscle of the pair pushes while the other pulls.
c. A single motor neuron can control both of them.
d. It allows the muscles to produce opposing movements.
Gravity would have the least effect on the movement of which of the following? (Explain your answer.)
a. A salmon
b. A snake
c. A sparrow
d. A grasshopper