Textbook Question
If the sequence of DNA in Question 12 were amplified using 25 PCR cycles, then the amount of this DNA would be predicted to increase by -fold.
905
views

 Freeman 7th Edition
Freeman 7th Edition Ch. 20 - The Molecular Revolution: Biotechnology, Genomics, and New Frontiers
Ch. 20 - The Molecular Revolution: Biotechnology, Genomics, and New Frontiers Problem 14
Problem 14 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


If the sequence of DNA in Question 12 were amplified using 25 PCR cycles, then the amount of this DNA would be predicted to increase by -fold.
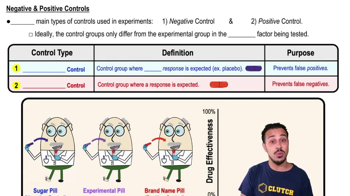
Why was it important to include a positive control and a negative control in the PCR analysis?
How could the research group determine whether a homologous gene for blight resistance exists in the human genome?