
Complete this concept map describing potential causes of evolutionary change within populations.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
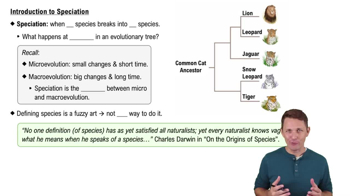
Microevolution
Genetic Drift

Natural Selection

Which of the following did not influence Darwin as he synthesized the theory of evolution by natural selection?
a. Examples of artificial selection that produce large and relatively rapid changes in domesticated species.
b. Lyell's Principles of Geology, on gradual geologic changes.
c. Comparisons of fossils with living organisms.
d. Mendel's paper describing the laws of inheritance.
Natural selection is sometimes described as 'survival of the fittest.' Which of the following best measures an organism's fitness?
a. How many fertile offspring it produces
b. How strong it is when pitted against others of its species
c. Its ability to withstand environmental extremes
d. How much food it is able to make or obtain
In an area of erratic rainfall, a biologist found that grass plants with alleles for curled leaves reproduced better in dry years, and plants with alleles for flat leaves reproduced better in wet years. This situation would tend to _________ . (Explain your answer.)
a. Cause genetic drift in the grass population.
b. Preserve genetic variation in the grass population.
c. Lead to stabilizing selection in the grass population.
d. Lead to uniformity in the grass population.
