Cytotoxic T cells are able to recognize infected body cells because
a. The infected cells display foreign antigens.
b. The infected cells produce antigens.
c. Infected cells release antibodies into the blood.
d. Helper T cells destroy them first.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


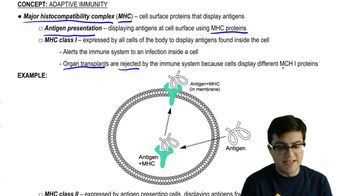
Cytotoxic T cells are able to recognize infected body cells because
a. The infected cells display foreign antigens.
b. The infected cells produce antigens.
c. Infected cells release antibodies into the blood.
d. Helper T cells destroy them first.
In the condition myasthenia gravis, antibodies bind to and block certain receptors on muscle cells, preventing muscle contraction. This condition is best classified as an
a. Immunodeficiency disorder.
b. Exaggerated immune reaction.
c. Allergic reaction.
d. Autoimmune disorder.
Which of the following statements is not true?
a. An antibody has more than one antigen-binding site.
b. An antigen can have different epitopes.
c. A lymphocyte has receptors for multiple and different antigens.
d. A bacterium has more than one antigen.