Complete this concept map to help you review some key concepts of genetics.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

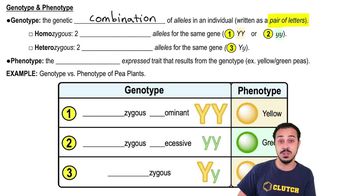

Complete this concept map to help you review some key concepts of genetics.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
Edward was found to be heterozygous (Ss) for sickle-cell trait. The alleles represented by the letters S and s are
a. Linked
b. On homologous chromosomes
c. Both present in each of Edward's sperm cells
d. On the same chromosome but far apart
Two fruit flies with eyes of the usual red color are crossed, and their offspring are as follows: 77 red-eyed males, 71 ruby-eyed males, 152 red-eyed females. The allele for ruby eyes is
a. Autosomal (carried on an autosome) and dominant
b. Autosomal and recessive
c. Sex-linked and dominant
d. Sex-linked and recessive
A man with type B blood and a woman who has type A blood could have children of which of the following phenotypes?
a. A or B only
b. AB only
c. AB or O
d. A, B, AB, or O