
What do the receptor cells in the lateral line system along the sides of a shark and the cochlea of your ear have in common?
a. They use hair cells to sense sound or pressure waves.
b. They are organs of equilibrium.
c. They use electromagnetic receptors to sense pressure waves in fluid.
d. They use granules that signal a change in position and stimulate their receptor cells.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Hair Cells
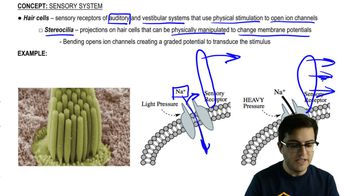
Lateral Line System

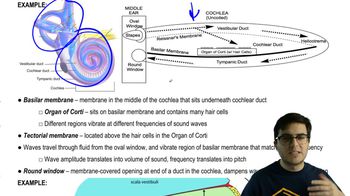
Cochlea
Which of the following sensory receptors is incorrectly paired with its category?
a. Hair cell . . . Mechanoreceptor
b. Taste receptor . . . Chemoreceptor
c. Rod . . . Electromagnetic receptor
d. Olfactory receptor . . . Electromagnetic receptor
Which of the following are not known to be present in human skin?
a. Thermoreceptors
b. Electromagnetic receptors
c. Pressure receptors
d. Pain receptors
If you look away from this book and focus your eyes on a distant object, the eye muscles _________ and the lenses _________ to focus images on the retinas.
a. Relax . . . Flatten
b. Relax . . . Become more rounded
c. Contract . . . Flatten
d. Contract . . . Become more rounded
Eighty-year-old Mr. Johnson was becoming slightly deaf. To test his hearing, his doctor held a vibrating tuning fork tightly against the back of Mr. Johnson's skull. This sent vibrations through the bones of the skull, setting the fluid in the cochlea in motion. Mr. Johnson could hear the tuning fork this way, but not when it was held away from the skull a few inches from his ear. The problem was probably in the _________ . (Explain your answer.)
a. Auditory nerve leading to the brain
b. Hair cells in the cochlea
c. Bones of the middle ear
d. Fluid of the cochlea
