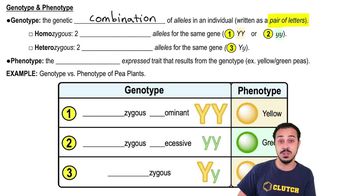
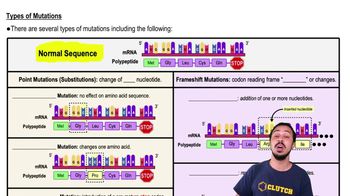
Textbook Question
Which of the following describes mutations? Select True or False for each statement.
T/F Point mutations can occur in any DNA sequence.
T/F Frameshift mutations can occur in any DNA sequence.
T/F Neutral mutations depend on the degeneracy of the genetic code.
T/F Deleterious mutations occur only in protein-coding sequences of DNA.
810
views