Textbook Question
In eukaryotes, what allows only certain genes to be expressed in different types of cells?
717
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
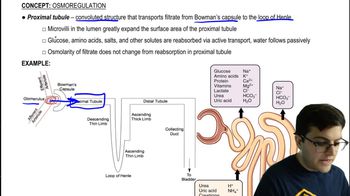
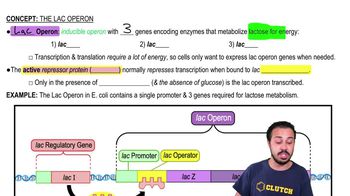

In eukaryotes, what allows only certain genes to be expressed in different types of cells?
Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(a) enhancers and the E. coli CAP binding site