
 Freeman 7th Edition
Freeman 7th Edition Ch. 20 - The Molecular Revolution: Biotechnology, Genomics, and New Frontiers
Ch. 20 - The Molecular Revolution: Biotechnology, Genomics, and New Frontiers Problem 2
Problem 2What is a plasmid?
a. An organelle found in many bacteria and certain eukaryotes
b. A circular DNA molecule that replicates independently of the main chromosome(s)
c. A type of virus that has a DNA genome and infects certain types of human cells, including lung and respiratory tract tissue
d. A type of virus that has an RNA genome, codes for reverse transcriptase, and inserts a cDNA copy of its genome into cells
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Plasmid
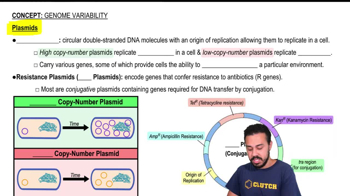
Independent Replication
Genetic Engineering

After finding a gene that causes a disease, researchers often introduce the defective allele into mice to create an animal model of the disease. Why are these models valuable?
a. They allow the testing of potential drug therapies without endangering human patients.
b. They allow the sequencing of the mutant allele.
c. They allow the production of large quantities of the defective gene product, usually a protein.
d. They allow the study of how the gene was transmitted from parents to offspring.
The human genome size is 3 billion base pairs, and the size of the baker's yeast genome, a single-celled organism, is 12 million base pairs. Therefore, the predicted genome size for another single-celled organism, an amoeba,
a. Is about the size of the human genome
b. Is about the size of the yeast genome
c. Is somewhere between the sizes of the yeast and human genomes
d. Cannot be predicted with any certainty
Explain how RNA-seq can be used to analyze patterns of gene expression.