- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2-. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the gas phase?
Determine the valence atomic orbitals of I and Cl involved in the construction of the MOs for ICl, an interhalogen compound, assuming it has molecular orbitals similar to the homonuclear diatomic molecule of F2
Using the molecular orbital diagram for Be2+, identify how the removal of an electron from the ion would change the bond order.
Provide the structure of the molecules AsF3 and AsF5 showing their spatial orientation. Identify which has a dipole moment and which does not and explain your answer.
Which statement is true?
Shown below are the critical temperatures for various organic compounds.

Using the given data, rank by decreasing order the critical pressures of C2H5F, C2H5Cl, and C2H5Br.
A 1.50 g of heptane (C7H16) with a vapor pressure of 35.5 torr at 20.0 °C is placed in a 2.50 L vessel at 20.0 °C. Assume that the vessel is closed and the volatile substance has reached equilibrium with its vapor, how much liquid heptane (in grams) is left?
The figure below shows the phase diagram of iodine. At a constant pressure of 2.0 atm, determine the phase change that occurs when the temperature of iodine is decreased from 488.15 K to 368.15 K.

Calculate the energy required to melt 7.23 kg of ice at 0°C if it was placed on the ground with a temperature of 26.0°C.
ΔHf,H2O = 80.0 cal/g
Which statement is true?
Indicate if the following are n-type or p-type semiconductors
(i) Ge doped with As
(ii) Si doped with B
(iii) Sn doped with Sb
Consider the unit cell of titanium(IV) oxide.
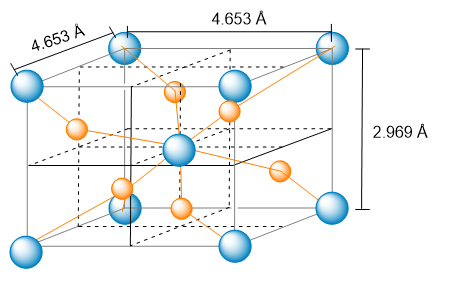
Identify the empirical formula.
A sample of metal was determined to have a density of 8.96 g/cm3. The metal crystallizes in a face-centered cubic cell and using X-ray diffraction the edge length was measured to be 362 pm. Determine the atomic weight, atomic radius, and identity of the metal.
Determine if water or hexane is the better solvent for the following solute.
Cl2, CsF, Naphthalene (C10H8), Methanol (CH3OH)
An aqueous solution is 23.0% acetic acid (CH₃COOH) by mass. Calculate the mole fraction of the solute and the molality of the solution.
What is the concentration of mercury in ppm if there are 321.4 μg mercury ions in a 4.50 L of water?
A solution of sucrose (342.3 g/mol) dissolved in water has a molarity of 0.819 M. What is the mole fraction of sucrose in the solution if the solution has a density of 0.997 g/mL?
Hydrochloric acid is used to neutralize the ammonia produced from a Kjeldahl method where all nitrogen organic substances are converted to ammonia. In a 4.37 g sample of organic material, 23.0 mL of 0.280 M HCl (aq) was used up. Determine the mass percentage of nitrogen in the sample.
NH3(aq) + HCl(aq) → NH4Cl(aq)
A solution is prepared by adding 50.0 g of NaNO3 to 50.0 g of H2O. It is stirred at 70°C until it becomes clear. Then, it is cooled down to 40°C where it is observed to be still clear. Select the statement that correctly describes the solution at 40°C. (Solubility of NaNO3 at 40°C is 102 g NaNO3 per 100 g H2O.)
When the temperature decreases, a gas in a liquid is _____ soluble and a solid in a liquid is ____ soluble.
A diver is using a 18/45 trimix, which means it's composed of 18% O2, 45% He and 37% N2, and dives to a depth of 40 m where the total pressure is 5.0 atm. Given that the Henry's law constant of N2 at 37 ºC is 1.0 × 10–3 mol/L atm, calculate the solubility of N2 in the blood at a depth of 40 m.
Determine the resulting equilibrium pressure above the liquid in a cylinder equipped with a movable piston when the volume of space above the liquid decreases from 400 mL to 200 mL at constant temperature. There is no air inside the cylinder and the equilibrium vapor pressure above the liquid is 40 mmHg.
38.2 g Na2SO4 (molar mass = 142.04 g/mol) is dissolved in 1470 g of water (Kb = 0.512 oC/m). What is the boiling point of the solution?
When 9.5 g of lithium stearate (LiC18H35O2, MW = 290.47 g/mol) is dissolved in 550 g benzene, the resulting solution freezes at 0.30 °C lower than pure benzene (FP = 5.5 °C). Calculate the value of Kf (freezing point constant) for benzene.
Assume that you have engineered a cell using a biosynthetic semipermeable membrane in a bioengineering laboratory. Instead of the usual 0.3 M ionic strength inside normal cells, this cell has an internal ionic strength of 0.45 M. The cell is submerged in a saline solution having an ionic strength of 0.30 M.
Initially, the volume of the cell is 5 µm3. Assuming there won't be any change in the volume of the solution outside the cell, what will be the volume of the cell after the system has come to equilibrium through osmosis?
For an aqueous solution containing 9.31 mg of lycopene (537 g/mol) in 5.12 mL of solution at 298 K, what osmotic pressure in mm Hg would you anticipate? What would the water column's height be in meters? The density of mercury is 13.534 g/mL at 298 K.
A solution of fructose in acetone has a vapor pressure of 204.0 mm Hg at 25.00 °C. Calculate the mass percent of fructose in the solution. Acetone has a vapor pressure of 231.0 mm Hg at 25.00 °C.