Textbook Question
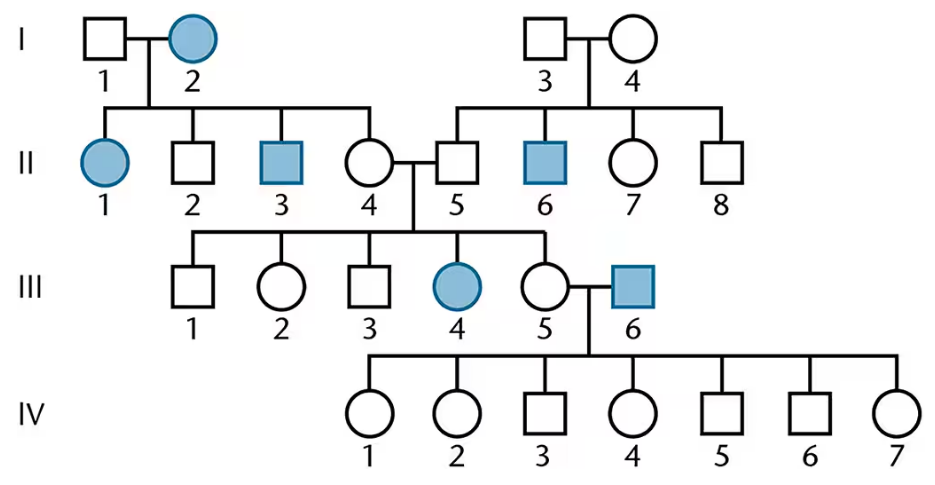
Draw all possible conclusions concerning the mode of inheritance of the trait portrayed in the following limited pedigree.
1084
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Draw all possible conclusions concerning the mode of inheritance of the trait portrayed in the following limited pedigree.
Draw all possible conclusions concerning the mode of inheritance of the trait portrayed in the following limited pedigree.
Draw all possible conclusions concerning the mode of inheritance of the trait portrayed in the following limited pedigree.